Page 34 - AN-1-2
P. 34
Advanced Neurology Role of Panax ginseng in neuronal complications
Table 2. Functional enrichments in PPIN network (KEGG 3.4. Docking study
Pathways)
Docking analyses revealed that compounds such as
Pathway Pathway description Count in False gensinside, panaxydol, panaxynol, and panaxytriol
ID gene set discovery rate exhibited low binding affinities (−4.37–−8), especially
00980 Metabolism of xenobiotics 3 0.000824 between gensinside and MAPK8, thereby indicating good
by cytochrome P450 binding efficiency between them. The quantity of H bonds
00982 Drug metabolism – 3 0.000824 of these respective four compounds with GSTP1, HSP90,
cytochrome P450 and MAPK8 is given in Tables 4 and 5 and Figure 4.
05204 Chemical carcinogenesis 3 0.000824
00480 Glutathione metabolism 2 0.0262 4. Discussion
The presence and role of various compounds found in
P. ginseng, such as stigmasterol, beta-sitosterol, inermin,
nepetin, aposiopolamine, celabenzine, panaxadiol,
panaxytriol, suchilactone, vulgarin, linoleic acid, alexandrin,
kaempferol, girinimbine, and ginsenoside, have been
associated with the bioactivity of the herb, as reported
by various studies over the years. The protective ability
of stigmasterol against cellular apoptosis, generation
of ROS, and the Ca levels in the mitochondria and
2+
cytosol in neuronal damage cells was studied, where it
was demonstrated that the compound was effective in
inhibiting the formation of malignant cells, along with
the decrease of the aforementioned activities on cellular
level. Moreover, stigmasterol plays a role in stimulating
apoptosis through the activation of the estrogen receptor
axis in the mitochondria. The migration of malignant
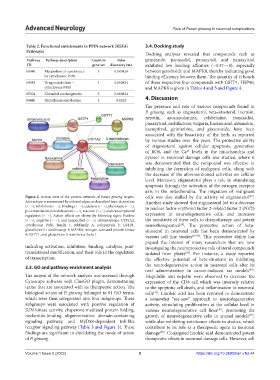
Figure 2. Action view of the protein network of Panax ginseng targets. cells was also stalled by the activity of stigmasterol .
[27]
Action type is represented by colored edges, as described here: Activation Another study showed that stigmasterol led to a decrease
(•-•), inhibition (•-•), binding (•-•), catalysis (•-•), phenotype (•-•), in nuclear factor-erythroid factor 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)
post-translational modification (•-•), reaction (•-•), and transcriptional
regulation (•-•). Action effects are shown by following signs: Positive expression in neurodegenerative cells, and increases
(•-•), negative (•-•), and unspecified (•-•). Abbreviations: CYP1A2, the sensitivity of these cells to chemotherapy and potent
[28]
cytochrome P450, family 1, subfamily A, polypeptide 2; GSTP1, neurotherapeutics . The protective action of beta-
glutathione S-transferase pi 1; MAPK8, mitogen-activated protein kinase sitosterol in neuronal cells has been demonstrated by
8; GSTT1, and glutathione S-transferase theta 1. various cell line studies [29-32] . This protective ability has
piqued the interest of many researchers that are now
including activation, inhibition, binding, catalysis, post- investigating the neuroprotective role of sterol compounds
translational modification, and their role in the regulation isolated from plants . For instance, a study reported
[33]
of transcription. the effective potential of beta-sitosterol in inhibiting
the neurodegenerative action in neuronal cells after its
3.3. GO and pathway enrichment analysis
oral administration in cancer-induced rat models .
[34]
The output of the network analysis was assessed through Hispidulin and nepetin were observed to decrease the
Cytoscape software with ClueGO plugin, demonstrating expression of the CD8 cell which was inversely relative
terms that are associated with its therapeutic action. The to the apoptotic cell death, and inflammation in neuronal
biological action of P. ginseng belonged to 91 GO terms, cells . Linoleic acid has been reported to demonstrate
[35]
which were then categorized into four subgroups. These a somewhat “see-saw” approach to neurodegenerative
subgroups were associated with positive regulation of activity, stimulating proliferation at the cellular level in
JUN kinase activity, chaperone-mediated protein folding, various neurodegenerative cell lines , promoting the
[36]
nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing growth of neurodegenerative cells in animal models ,
[37]
signaling pathway, and MyD88-dependent toll-like while also exhibiting anti-tumor effects in studies, which
receptor signaling pathway (Table 3 and Figure 3). These contribute to its role as a therapeutic agent in neuronal
findings are significant in elucidating the mode of action damage . Conjugated linoleic acid demonstrated potent
[38]
of P. ginseng. therapeutic effects in neuronal damage cells. However, cell
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.v1i2.44