Page 23 - AN-2-4
P. 23
Advanced Neurology Futile recanalization of acute basilar artery occlusion
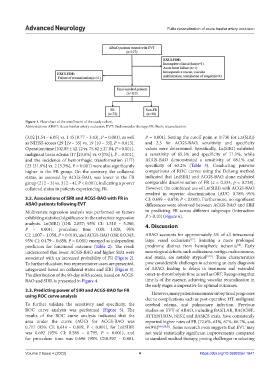
Figure 1. Flow chart of the enrollment of the study cohort.
Abbreviations: ABAO: Acute basilar artery occlusion; EVT: Endovascular therapy; FR: Futile recanalization.
(3.02 [1.54 – 6.05] vs. 1.45 [0.77 – 3.43], P = 0.001), as well P = 0.001). Setting the cutoff point at 0.730 for Ln(SIRI)
as NIHSS scores (29 [19 – 35] vs. 19 [10 – 35], P = 0.013). and 2.5 for ACGS-BAO, sensitivity and specificity
Operation time (102.85 ± 42.12 vs. 75.82 ± 27.84, P = 0.001), values were determined. Specifically, Ln(SIRI) exhibited
malignant brain edema (17 [23.6%] vs. 0 [0%]), P = 0.001), a sensitivity of 65.3% and specificity of 71.1%, while
and the incidence of hemorrhagic transformation (HT) ACGS-BAO demonstrated a sensitivity of 68.1% and
(23 [31.9%] vs. 2 [5.3%], P = 0.001) were also significantly specificity of 63.2% (Table 3). Conducting pairwise
higher in the FR group. On the contrary, the collateral comparisons of ROC curves using the DeLong method
status, as assessed by ACGS-BAO, was lower in the FR indicated that Ln(SIRI) and ACGS-BAO alone exhibited
group (2 [2 – 3] vs. 3 [2 – 4], P < 0.001), indicating a poorer comparable discrimination of FR (z = 0.334, p = 0.738).
collateral status in patients experiencing FR. However, the combined use of Ln(SIRI) with ACGS-BAO
resulted in superior discrimination (AUC: 0.789; 95%
3.2. Associations of SIRI and ACGS-BAO with FR in CI: 0.699 – 0.878; P < 0.001). Furthermore, no significant
ABAO patients following EVT differences were observed between ACGS-BAO and SIRI
Multivariate regression analysis was performed on factors in predicting FR across different subgroups (interaction
exhibiting statistical significance in the univariate regression P > 0.10) (Figure 6).
analysis. Ln(SIRI) (OR: 2.857; 95% CI: 1.518 – 5.380, 4. Discussion
P = 0.001), procedure time (OR: 1.028; 95%
CI: 1.007 – 1.050, P = 0.010), and ACGS-BAO (OR: 0.0.343; ABAO accounts for approximately 5% of all intracranial
[17]
95% CI: 0.179 – 0.658, P = 0.001) emerged as independent large vessel occlusions , featuring a more prolonged
[18]
predictors for functional outcome (Table 2). The result prodrome distinct from hemispheric ischemia . Early
underscored that lower ACGS-BAO and higher SIRI were neurological deficits, such as dizziness, vertigo, maliciousness,
associated with an increased probability of FR (Figure 2). and ataxia, are notably atypical [2,19] . These characteristics
To further elucidate, two representative cases are presented, pose considerable challenges in achieving an early diagnosis
categorized based on collateral status and SIRI (Figure 3). of ABAO, leading to delays in treatment and extended
The distribution of the 90-day mRS scores, based on ACGS- onset-to-thrombolysis time as well as ORT. Recognizing that
BAO and SIRI, is presented in Figure 4. time is of the essence, achieving vascular recanalization in
the early stages is imperative for optimal outcomes.
3.3. Predicting power of SIRI and ACGS-BAO for FR
using ROC curve analysis However, many patients encounter suboptimal prognoses
due to complications such as post-operative HT, malignant
To further validate the sensitivity and specificity, the cerebral edema, and pulmonary infection. Previous
ROC curve analysis was performed (Figure 5). The studies on EVT of ABAO, including BASILAR, BAOCHE,
results of the ROC curve analysis indicated that the ATTENTION, BEST, and BASICS trials, have consistently
area under the curve (AUC) for ACGS-BAO was reported higher rates of FR (72.6%, 61%, 67%, 66.7%, and
0.717 (95% CI: 0.614 – 0.819, P < 0.001), for Ln(SIRI) 64.9%) [4-6,20,21] . Some research even suggests that EVT may
was 0.692 (95% CI: 0.589 – 0.795, P = 0.001), and not yield statistically significant improvements compared
for procedure time was 0.696 (95% CI:0.592 – 0.801, to standard medical therapy, posing challenges in selecting
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.1641