Page 27 - AN-2-4
P. 27
Advanced Neurology Futile recanalization of acute basilar artery occlusion
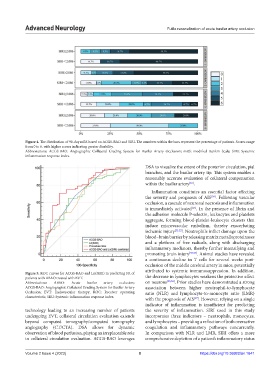
Figure 4. The distribution of 90-day mRS based on ACGS-BAO and SIRI. The numbers within the bars represent the percentage of patients. Scores range
from 0 to 6, with higher scores indicating greater disability.
Abbreviations: ACGS-BAO: Angiographic Collateral Grading System for Basilar Artery Occlusion; mRS: modified Rankin Scale; SIRI: Systemic
inflammation response index.
DSA to visualize the extent of the posterior circulation, pial
branches, and the basilar artery tip. This system enables a
reasonably accurate evaluation of collateral compensation
within the basilar artery .
[16]
Inflammation constitutes an essential factor affecting
the severity and prognosis of AIS . Following vascular
[30]
occlusion, a cascade of neuronal necrosis and inflammation
is immediately activated . In the presence of fibrin and
[13]
the adhesion molecule P-selectin, leukocytes and platelets
aggregate, forming blood-platelet-leukocyte clusters that
induce microvascular embolism, thereby exacerbating
ischemic injury [31,32] . Neutrophils inflict damage upon the
blood–brain barrier by releasing matrix metalloproteinases
and a plethora of free radicals, along with discharging
inflammatory mediators, thereby further intensifying and
promoting brain injury [33,34] . Animal studies have revealed
a continuous decline in T cells for several weeks post-
occlusion of the middle cerebral artery in mice, potentially
attributed to systemic immunosuppression. In addition,
Figure 5. ROC curves for ACGS-BAO and Ln(SIRI) in predicting FR of
patients with ABAO treated with EVT. the decrease in lymphocytes weakens the protective effect
Abbreviations: ABAO: Acute basilar artery occlusion; on neurons [35,36] . Prior studies have demonstrated a strong
ACGS-BAO: Angiographic Collateral Grading System for Basilar Artery association between higher neutrophil-to-lymphocyte
Occlusion; EVT: Endovascular therapy; ROC: Receiver operating ratio (NLR) and lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR)
characteristic; SIRI: Systemic inflammation response index.
with the prognosis of AIS . However, relying on a single
[37]
indicator of inflammation is insufficient for predicting
technology leading to an increasing number of patients the severity of inflammation. SIRI used in this study
undergoing EVT, collateral circulation evaluation extends incorporates three indicators – neutrophils, monocytes,
beyond computed tomography/computed tomography and lymphocytes – providing a reflection of both overactive
angiography (CT/CTA). DSA allows for dynamic coagulation and inflammatory pathways concurrently.
observation of blood perfusion, playing an irreplaceable role In comparison with NLR and LMR, SIRI offers a more
in collateral circulation evaluation. ACGS-BAO leverages comprehensive depiction of a patient’s inflammatory status
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.1641