Page 26 - AN-2-4
P. 26
Advanced Neurology Futile recanalization of acute basilar artery occlusion
A B C D
E F G H
I J K L
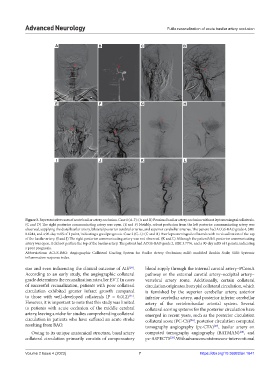
Figure 3. Representative cases of acute basilar artery occlusion. Case 1 (A-F): (A and B) Proximal basilar artery occlusion without leptomeningeal collaterals.
(C and D) The right posterior communicating artery was open. (E and F) Notably, robust perfusion from the left posterior communicating artery was
observed, supplying the distal basilar artery, bilateral posterior cerebral arteries, and superior cerebellar arteries. The patient had ACGS-BAO grade 4, SIRI
0.6244, and a 90-day mRS of 1 point, indicating a good prognosis. Case 2 (G-L): (G and H) Poor leptomeningeal collaterals with no visualization of the top
of the basilar artery. (I and J) The right posterior communicating artery was not observed. (K and L) Although the patient’s left posterior communicating
artery was open, it did not perfuse the top of the basilar artery. The patient had ACGS-BAO grade 2, SIRI 3.7776, and a 90-day mRS of 4 points, indicating
a poor prognosis.
Abbreviations: ACGS-BAO: Angiographic Collateral Grading System for Basilar Artery Occlusion; mRS: modified Rankin Scale; SIRI: Systemic
inflammation response index.
size and even influencing the clinical outcome of AIS . blood supply through the internal carotid artery–PComA
[24]
According to an early study, the angiographic collateral pathway or the external carotid artery–occipital artery–
grade determines the recanalization rate after EVT. In cases vertebral artery route. Additionally, certain collateral
of successful recanalization, patients with poor collateral circulation originates from pial collateral circulation, which
circulation exhibited greater infarct growth compared is furnished by the superior cerebellar artery, anterior
to those with well-developed collaterals (P = 0.012) . inferior cerebellar artery, and posterior inferior cerebellar
[25]
However, it is important to note that this study was limited artery of the vertebrobasilar arterial system. Several
to patients with acute occlusion of the middle cerebral collateral scoring systems for the posterior circulation have
artery, leaving a niche for studies comprehending collateral emerged in recent years, such as the posterior circulation
circulation in patients who have suffered an acute stroke collateral score (PC-CS) , posterior circulation computed
[26]
resulting from BAO. tomography angiography (pc-CTA) , basilar artery on
[27]
Owing to its unique anatomical structure, basal artery computed tomography angiography (BATMAN) , and
[28]
collateral circulation primarily consists of compensatory pc-ASPECTS . With advancements in neuro-interventional
[29]
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/an.1641