Page 92 - AN-4-1
P. 92
Advanced Neurology Tetrapleura tetraptera protects the hippocampus
A B
C D
Figure 3. Nissl-stained cell count of the cornu ammonis 3 region of the
hippocampus. A repeated measures analysis of variance and post-hoc tests
were performed. Values are expressed as mean±standard error of the mean.
Notes: ***Indicates significant difference from the control group
at p<0.001. b,d,e,f Significantly different from TT, PTZ+SV, PTZ+TT
(low), and PTZ+TT (int), respectively, at p<0.05. Sample size per
group: Control=3; TT=3; PTZ=3; PTZ+SV=3; PTZ+TT (low)=3;
E F PTZ+TT (int)=3; PTZ+TT (high)=3.
Abbreviations: PTZ: pentylenetetrazol; SV: Sodium valproate;
TT: Tetrapleura tetraptera.
groups (Figure 6A and B). The PTZ group exhibited slightly
reduced GFAP expression in the hippocampal CA3 region
compared to the control group (Figure 6C). In contrast, the
hippocampal CA3 regions of the groups pre-treated with
G sodium valproate, as well as the low, intermediate, and
high doses of T. tetraptera, showed less GFAP expression
compared to the control group (Figure 6D-G).
A repeated measures analysis of variance and post-hoc
tests revealed that the number of GFAP-labeled cells was
significantly lower (p<0.05) in the T. tetraptera-alone group,
as well as in the sodium valproate, intermediate-dose, and
high-dose T. tetraptera-pretreatment groups, compared
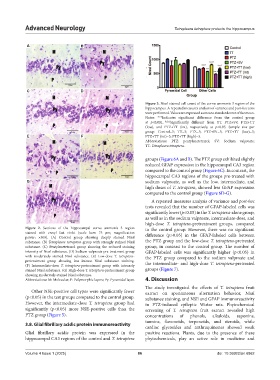
Figure 2. Sections of the hippocampal cornu ammonis 3 region to the control group. However, there was no significant
stained with cresyl fast violet (scale bars: 75 μm; magnification difference (p>0.05) in the GFAP-labeled cells between
power: ×400). (A) Control group showing deeply stained Nissl
substance. (B) Tetrapleura tetraptera group with strongly stained Nissl the PTZ group and the low-dose T. tetraptera-pretreated
substance. (C) Pentylenetetrazol group showing the reduced staining group, in contrast to the control group. The number of
intensity of Nissl substance. (D) Sodium valproate pre-treatment group GFAP-labeled cells was significantly higher (p<0.05) in
with moderately stained Nissl substance. (E) Low-dose T. tetraptera- the PTZ group compared to the sodium valproate and
pretreatment group showing less intense Nissl substance staining. the intermediate- and high-dose T. tetraptera-pretreated
(F) Intermediate-dose T. tetraptera-pretreatment group with intensely
stained Nissl substance. (G) High-dose T. tetraptera-pretreatment group groups (Figure 7).
showing moderately stained Nissl substance.
Abbreviations: M: Molecular; P: Polymorphic layers; Py: Pyramidal layer. 4. Discussion
The study investigated the effects of T. tetraptera fruit
Other NSE-positive cell types were significantly fewer extract on spontaneous alternation behavior, Nissl
(p<0.05) in the test groups compared to the control group. substance staining, and NSE and GFAP immunoreactivity
However, the intermediate-dose T. tetraptera group had in PTZ-induced epileptic Wistar rats. Phytochemical
significantly (p<0.05) more NSE-positive cells than the screening of T. tetraptera fruit extract revealed high
PTZ group (Figure 5). concentrations of phenols, alkaloids, saponins,
tannins, flavonoids, terpenoids, and steroids, while
3.8. Glial fibrillary acidic protein immunoreactivity
cardiac glycosides and anthraquinones showed weak
Glial fibrillary acidic protein was expressed in the positive reactions. Plants, due to the presence of these
hippocampal CA3 regions of the control and T. tetraptera phytochemicals, play an active role in medicine and
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 86 doi: 10.36922/an.6862