Page 93 - AN-4-1
P. 93
Advanced Neurology Tetrapleura tetraptera protects the hippocampus
A B
C D
Figure 5. Neuron-specific enolase-positive cell count in the hippocampal
cornu ammonis 3 region of the experimental groups. A repeated measures
analysis of variance and Tukey’s post-hoc tests were performed. Values
are expressed as mean±standard error of the mean. Notes: Sample size
of per group: Control=3; TT=3; PTZ=3; PTZ+SV=3; PTZ+TT (low)=3;
PTZ+TT (int)=3; PTZ+TT (high)=3. *,**, and ***Indicate significant
E F differences from the control at p<0.05, p<0.01, and p<0.001, respectively.
b,c,e,f,g Significantly different from TT, PTZ, PTZ+TT (low), PTZ+TT (int),
and PTZ+TT (high), respectively, at p<0.05.
Abbreviations: PTZ: pentylenetetrazol; SV: Sodium valproate;
TT: Tetrapleura tetraptera.
A B
G
C D
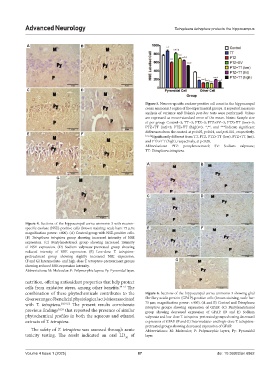
Figure 4. Sections of the hippocampal cornu ammonis 3 with neuron-
specific enolase (NSE)-positive cells (brown staining; scale bars: 75 μm; E F
magnification power: ×400). (A) Control group with NSE-positive cells.
(B) Tetrapleura tetraptera group showing increased intensity of NSE
expression. (C) Pentylenetetrazol group showing increased intensity
of NSE expression. (D) Sodium valproate-pretreated group showing
reduced intensity of NSE expression. (E) Low-dose T. tetraptera-
pretreatment group showing slightly increased NSE expression.
(F and G) Intermediate- and high-dose T. tetraptera-pretreatment groups G
showing reduced NSE expression intensity.
Abbreviations: M: Molecular; P: Polymorphic layers; Py: Pyramidal layer.
nutrition, offering antioxidant properties that help protect
cells from oxidative stress, among other benefits. 49-51 The
combination of these phytochemicals contributes to the Figure 6. Sections of the hippocampal cornu ammonis 3 showing glial
diverse range of beneficial physiological activities associated fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-positive cells (brown staining; scale bar:
with T. tetraptera. 28,31,52 The present results corroborate 75 μm; magnification power: ×400). (A and B) Control and Tetrapleura
tetraptera groups showing expression of GFAP. (C) Pentylenetetrazol
previous findings 52,53 that reported the presence of similar group showing decreased expression of GFAP. (D and E) Sodium
phytochemical profiles in both the aqueous and ethanol valproate and low-dose T. tetraptera-pretreated groups showing decreased
extracts of T. tetraptera. expression of GFAP. (F and G) Intermediate- and high-dose T. tetraptera-
pretreated groups showing decreased expression of GFAP.
The safety of T. tetraptera was assessed through acute Abbreviations: M: Molecular; P: Polymorphic layers; Py: Pyramidal
toxicity testing. The result indicated an oral LD of layer.
50
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 87 doi: 10.36922/an.6862