Page 94 - AN-4-1
P. 94
Advanced Neurology Tetrapleura tetraptera protects the hippocampus
findings suggest that the administered doses of T. tetraptera
possess anticonvulsant activity, potentially reducing the
severity of PTZ-induced seizures, a result consistent
with a previous report. Although the exact mechanism
36
underlying T. tetraptera’s anticonvulsant effect remains
to be elucidated, it is likely mediated through GABAergic
transmission. This hypothesis is supported by a prior study
indicating that alkaloids and flavonoids, which are also
61
constituents of T. tetraptera, enhance GABA transmission.
Pentylenetetrazol administration resulted in mortality,
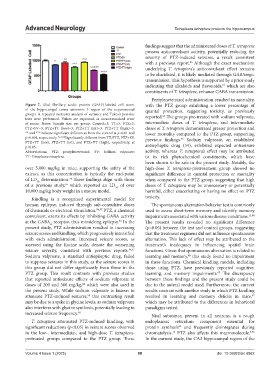
Figure 7. Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-labeled cell count with the PTZ group exhibiting a lower percentage of
of the hippocampal cornu ammonis 3 region of the experimental quantal protection, suggesting toxicity, as previously
groups. A repeated measures analysis of variance and Tukey’s post-hoc reported. The groups pre-treated with sodium valproate,
62
tests were performed. Values are expressed as mean±standard error
of mean. Notes: Sample size per group: Control=3; TT=3; PTZ=3; intermediate doses of T. tetraptera, and intermediate
PTZ+SV=3; PTZ+TT (low)=3; PTZ+TT (int)=3; PTZ+TT (high)=3. doses of T. tetraptera demonstrated greater protection and
** and ***indicate significant differences from the control at p<0.01 and lower mortality compared to the PTZ group, supporting
p<0.001, respectively. b,c,d,e,f Significantly different from TT, PTZ, PTZ+SV, previous findings. Sodium valproate, an established
36
PTZ+TT (low), PTZ+TT (int), and PTZ+TT (high), respectively, at
p<0.05. antiepileptic drug (54), exhibited expected antiseizure
Abbreviations: PTZ: pentylenetetrazol; SV: Sodium valproate; activity, whereas T. tetraptera’s effect may be attributed
TT: Tetrapleura tetraptera. to its rich phytochemical constituents, which have
been shown to be safe in the present study. Notably, the
over 5,000 mg/kg in mice, supporting the safety of the high-dose T. tetraptera-pretreatment group showed no
extract, as this concentration is typically the end-point significant difference in quantal protection or mortality
of LD determination. These findings align with those when compared to the PTZ group, suggesting that high
54
50
of a previous study, which reported an LD of over doses of T. tetraptera may be unnecessary or potentially
55
50
10,000 mg/kg body weight in a mouse model. harmful, either exacerbating or having no effect on PTZ
Kindling is a recognized experimental model for toxicity.
human epilepsy, induced through sub-convulsive doses The spontaneous alternation behavior test is commonly
of chemicals or electrical stimulation. 56,57 PTZ, a chemical used to assess short-term memory and identify memory
convulsant, exerts its effects by inhibiting GABA activity impairments associated with various disease conditions. 11,48
at the GABA receptor, thus mimicking epilepsy. In the The present results revealed no significant difference
58
A
present study, PTZ administration resulted in increasing (p>0.05) between the test and control groups, suggesting
seizure scores and kindling, which progressively intensified that the treatment regimens did not influence spontaneous
with each administration. Increased seizure scores, as alternation. This lack of effect may be attributed to the
assessed using the Racine scale, denote the worsening treatment’s inadequacy in influencing spatial brain
seizure severity, consistent with previous reports. 45,57 functions. Given that spontaneous alternation is related to
Sodium valproate, a standard antiepileptic drug, failed learning and memory, this study found no impairment
48
to suppress seizures in this study, as the seizure scores in in these functions. Chemical kindling models, including
this group did not differ significantly from those in the those using PTZ, have previously reported cognitive,
PTZ group. This result contrasts with previous studies learning, and memory impairments. The discrepancy
63
that reported antiseizure effects of sodium valproate at between these findings and the present study could be
doses of 200 and 300 mg/kg, which were also used in due to the animal model used. Furthermore, the current
44
the present study. While sodium valproate is known to results contrast with another study in which PTZ kindling
attenuate PTZ-induced seizures, this contrasting result resulted in learning and memory deficits in mice,
57
59
may be due to a spike in glycine levels, as sodium valproate which may be attributed to the differences in behavioral
also interferes with glycine synthesis, potentially leading to paradigms tested.
increased seizure frequency. 60 Nissl substance, present in all neurons, is a rough
T. tetraptera attenuated PTZ-induced kindling, with endoplasmic reticulum component essential for
significant reductions (p<0.05) in seizure scores observed protein synthesis and frequently disintegrates during
64
in the low-, intermediate-, and high-dose T. tetraptera- chromatolysis. PTZ also affects this macromolecule.
16
9,56
pretreated groups compared to the PTZ group. These In the current study, the CA3 hippocampal region of the
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 88 doi: 10.36922/an.6862