Page 96 - AN-4-2
P. 96
Advanced Neurology PVT in Indonesian neurological patients
per subgroup for determining specificity. There were no analyzed using the Spearman correlation due to their non-
37
missing data in this study. Demographic variables (age, normal distribution. The effect size was determined using
44
education, and gender) were compared between groups. r, with r = 0.10 indicating a small effect, r = 0.30 indicating
MMSE scores in the ND and PS groups were calculated a medium effect, and r = 0.50 indicating a large effect.
39
and compared. The mean PVT scores for each group The data are available through the Donders repository.
were compared using the Kruskal–Wallis test due to the Analyses were performed using JASP 0.16.3. 45
non-normal distribution of all PVTs across the groups
(Shapiro–Wilk P < 0.05), followed by post hoc Mann– 3. Results
38
Whitney U-tests with Bonferroni correction and their As shown in Table 1, significant differences were observed
corresponding effect sizes (r). 39,40 In addition, participants between the clinical groups in terms of age. As expected,
with ND were divided into mild (MMSE score ≥22) and the ND group was the oldest and had a significantly lower
major (MMSE score <22) ND groups, as distinct PVT cut- MMSE score than the PS group. No significant differences
41
off scores might apply to these groups. Diagnostic accuracy were found between the clinical groups regarding
was evaluated in each group by examining the specificity educational level and gender distribution, although the
of the recommended cut-off scores from a previous ND group had a slightly lower educational level compared
simulation study. Participants who performed below the to the other two groups. The clinical groups also differed
22
specific cut-off score were considered false positives. If the significantly on all PVT scores, as shown in Table 2. The
obtained specificity was below the acceptable threshold ND group performed significantly worse than the other
(<0.90), the cut-off scores were adjusted (i.e., lowered) to clinical groups on all PVTs, except for the RDS, with
ensure a specificity rate of at least 0.90, as higher specificity medium-to-large effects (r range = 0.29 – 0.55; Table 3).
is essential for PVTs. 14,42,43 For the NV-MSVT, the specificity No significant differences were found between the PVT
rate was calculated by dividing the number of participants scores of the PS and mixed-etiology groups. In addition,
failing at least one of the A criteria and at least two of the the mild ND group scored significantly higher than the
B criteria (indicating probable invalid performance) by the major ND group on all PVTs, with medium to medium-
total number of participants in each group, as suggested by to-large effects (r range = 0.38 – 0.50; Table 4).
the NV-MSVT manual. 26
The results presented in Table 5 indicate that the cut-
The adjusted cut-off scores for each PVT were used to off scores from the previous simulation study resulted in
calculate the number of participants failing at least two unacceptably low specificity rates (<0.90) for all PVTs.
PVTs. Failure on the embedded validities of DS (e.g., failure Therefore, we adjusted the cut-off scores for use in clinical
on RDS and LDF-2) was considered a single PVT failure, samples. For the RDS, LDF-1, and LDF-2, the PS and
as they are derived from the same test, as reflected by mixed-etiology groups achieved specificity rates of at least
13
their high intercorrelation in this study. The demographic 0.90 using the adjusted cut-off scores of ≤4, ≤3, and ≤2,
characteristics of the participants failing at least two PVTs respectively. A more significant adjustment of the cut-
were then presented. off scores in the RDS, LDF-1, and LDF-2 was required
Intercorrelation analyses were performed between for the ND group, with cut-off scores decreased to ≤3,
PVT scores, demographic variables (i.e., gender, age, and ≤2, and ≤1, respectively. However, similar to the PS and
education), and MMSE scores (for participants with ND mixed-etiology groups, the adjusted cut-off score for the
and PS groups only). The point-biserial correlation was LDF-2 in the mild ND group was ≤2. For the TMJPI, the
used for the gender variable, while the other variables were mixed-etiology group required the least adjustment to
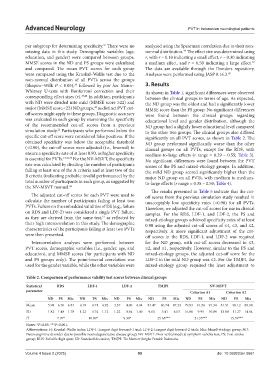
Table 2. Comparison of performance validity test scores between clinical groups
Statistical RDS LDF‑1 LDF‑2 TMJPI NV‑MSVT
parameter Criterion A1 Criterion A2
ND PS Mix ND PS Mix ND PS Mix ND PS Mix ND PS Mix ND PS Mix
Mean 5.98 6.76 6.81 4.18 4.71 4.92 3.37 4.00 4.04 81.47 86.74 87.23 79.83 91.24 91.34 81.51 90.12 88.98
SD 1.82 1.48 1.78 1.22 0.74 1.12 1.22 0.94 1.00 9.63 5.41 6.03 16.08 9.95 10.89 13.88 11.27 14.94
H 7.97* 10.89* 9.30* 25.65*** 21.35*** 15.59***
Notes: *P<0.05; ***P<0.001.
Abbreviations: H: Kruskal-Wallis index; LDF-1: Longest digit forward-1 trial; LDF-2: Longest digit forward-2 trials; Mix: Mixed-etiology group; ND:
Neurocognitive disorder due to possible neurodegenerative disease group; NV-MSVT: Non-verbal medical symptom validity test; PS: Post-stroke
group; RDS: Reliable digit span; SD: Standard deviation; TMJPI: Tes Memori Jangka Pendek Indonesia.
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 90 doi: 10.36922/an.5661