Page 99 - AN-4-3
P. 99
Advanced Neurology TG100-115 suppresses glioblastoma cell functions
A
B
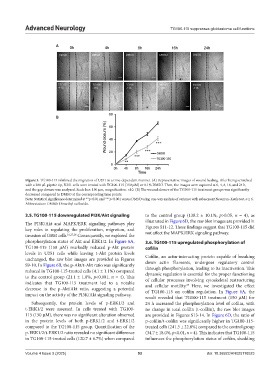
Figure 3. TG100-115 inhibited the migration of U251 in a time-dependent manner. (A) Representative images of wound healing. After being scratched
with a 200 µL pipette tip, U251 cells were treated with TG100-115 (150 µM) or 0.1% DMSO. Then, the images were captured at 0, 4, 8, 16, and 24 h,
and the gap closure was analyzed. Scale bar: 150 µm, magnification: ×10. (B) The wound closure of the TG100-115 treatment groups was significantly
decreased compared to DMSO at the corresponding time points.
Note: Statistical significance determined at **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 versus DMSO using one-way analysis of variance with subsequent Newman–Keuls test, n ≥ 6.
Abbreviation: DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide.
3.5. TG100-115 downregulated PI3K/Akt signaling to the control group (138.2 ± 10.1%, p>0.05, n = 4), as
illustrated in Figure 6D, the raw blot images are provided in
The PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways play
key roles in regulating the proliferation, migration, and Figures S11-12. These findings suggest that TG100-115 did
invasion of GBM cells. 16,27,28 Consequently, we explored the not affect the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway.
phosphorylation status of Akt and ERK1/2. In Figure 6A, 3.6. TG100-115 upregulated phosphorylation of
TG100-115 (150 µM) markedly reduced p-Akt protein cofilin
levels in U251 cells while leaving t-Akt protein levels
unchanged, the raw blot images are provided in Figures Cofilin, an actin-interacting protein capable of breaking
S9-10. In Figure 6B, the p-Akt/t-Akt ratio was significantly down actin filaments, undergoes regulatory control
through phosphorylation, leading to its inactivation. This
reduced in TG100-115-treated cells (4.1 ± 1.1%) compared
to the control group (21.1 ± 1.8%, p<0.001, n = 4). This dynamic regulation is essential for the proper functioning
of cellular processes involving cytoskeletal restructuring
indicates that TG100-115 treatment led to a notable 29
decrease in the p-Akt/Akt ratio, suggesting a potential and cellular motility. Here, we investigated the effect
of TG100-115 on cofilin regulation. In Figure 6A, the
impact on the activity of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
result revealed that TG100-115 treatment (150 µM) for
Subsequently, the protein levels of p-ERK1/2 and 24 h increased the phosphorylation level of cofilin, with
t-ERK1/2 were assessed. In cells treated with TG100- no change in total cofilin (t-cofilin), the raw blot images
115 (150 µM), there was no significant alteration observed are provided in Figures S13-14. In Figure 6D, the ratio of
in the protein levels of both p-ERK1/2 and t-ERK1/2 p-cofilin/t-cofilin was significantly higher in TG100-115-
compared to the TG100-115 group. Quantification of the treated cells (241.5 ± 22.8%) compared to the control group
p-ERK1/2/t-ERK1/2 ratio revealed no significant difference (34.7 ± 18.0%, p<0.01, n = 4). This indicates that TG100-115
in TG100-115-treated cells (120.7 ± 6.7%) when compared influences the phosphorylation status of cofilin, shedding
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 93 doi: 10.36922/AN025110023