Page 70 - ARNM-2-3
P. 70
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Association between PET-derived flows and angiography
1. Introduction 690, GE Healthcare, USA). The stress and imaging
protocols used have been described in previous work by
Positron emission tomography (PET) myocardial perfusion our group. 17
imaging (MPI) is highly accurate for the diagnosis of
coronary artery disease (CAD) and risk assessment. Multiple 2.2. QCA
1
studies have evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of PET
MPI in CAD, demonstrating that the sensitivity of PET for Standard coronary angiographic images were analyzed
detecting obstructive CAD is 92% and 95% for single-vessel with at least two projections obtained per vessel
and multivessel CAD, respectively. PET also allows for distribution and angles of projection optimized for
2-5
non-invasive quantification of absolute global and regional the cardiac position. In each patient, luminal diameter
myocardial blood flow (MBF; expressed as ml/min/g) and stenoses of the major epicardial coronary arteries were
myocardial flow reserve (MFR; ratio of stress/rest MBF) using clinically graded by subjective visual consensus of two
tracers such as rubidium-82 ( Rb). Measurement of MBF experienced operators and then analyzed using two-
82
has been shown to improve diagnostic accuracy and provides dimensional QCA at the Yale Cardiovascular Research
incremental prognostic information compared to measures of Group Angiographic Core Laboratory (QAngio XA;
relative perfusion alone, particularly in multivessel disease. 6-10 7.4 MEDIS, Netherlands), which was applied to both
obstructive and non-obstructive atherosclerotic plaques
Global and regional MBF are also important from the reference vessel. Either isocenter or catheter
prognostic tools in patients with and without obstructive calibration was applied. Coronary lesions were analyzed
CAD. 9,11-16 PET MPI with MBF quantification is the non- for qualitative atherosclerotic plaque characteristics.
invasive gold-standard modality for the diagnosis of Diameter and length (mm) of obstruction and area
coronary microvascular dysfunction by quantifying (mm ), along with percent stenosis, were measured and
10
2
reductions in hyperemic MBF and/or MFR, thus avoiding then compared to visual stenosis grading. Percent stenosis
10
costly and repeated invasive testing.
was calculated as:
Despite all the advances in the understanding of
invasive and non-invasive coronary physiology assessment ([1-minimal lumen diameter]/reference vessel
and global Rb-derived MBF, there is a paucity of data on diameter) × 100 (I)
82
the correlation between regional MBF and angiographic Other characteristics, such as symmetry and area of
severity of CAD, its implications for revascularization, and plaque and the distal and proximal stenosis measurements
its relationship to all-cause mortality. To date, there are no were also obtained. All traced lesions were manually
large studies evaluating the correlation between regional
MBF/MFR and angiographic stenoses to validate its
widespread use for referral for invasive procedures. With
this background, our study seeks to determine the relation
between Rb-derived regional MBF indices and percent
82
area stenosis through quantitative coronary angiography
(QCA), and their relationship to all-cause mortality.
2. Methods
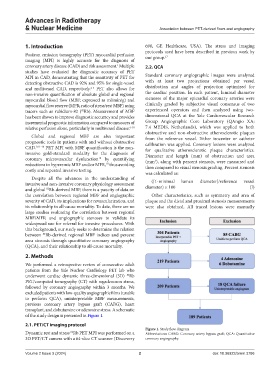
We performed a retrospective review of consecutive adult
patients from the Yale Nuclear Cardiology PET lab who
82
underwent cardiac dynamic three-dimensional (3D) Rb
PET/computed tomography (CT) with regadenoson stress,
followed by coronary angiography within 3 months. We
excluded patients with low-quality angiographic films (unable
to perform QCA), uninterpretable MBF measurements,
previous coronary artery bypass graft (CABG), heart
transplant, and dobutamine or adenosine stress. A schematic
of the study design is presented in Figure 1.
2.1. PET/CT imaging protocol
Figure 1. Study flow diagram
Dynamic rest and stress Rb PET MPI was performed on a Abbreviations: CABG: Coronary artery bypass graft; QCA: Quantitative
82
3D PET/CT camera with a 64-slice CT scanner (Discovery coronary angiography.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2024) 2 doi: 10.36922/arnm.3786