Page 94 - ARNM-3-1
P. 94
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Nanomaterials in cancer chemoimmunotherapy
have been designed and studied for use as vectors in of differentiation 8-positive (CD8 ) cytotoxic T cells.
+
chemoimmunotherapy, including lipid nanocarriers, In addition, heme oxygenase-1 inhibition alters tumor
22
polymeric nanocarriers, dendrimers, metallic and macrophage differentiation. In a recent study, glutathione-
23
24
inorganic nanoparticles, and biomimetic nanoparticles responsive prodrug-based hybrid lipid-polymer
25
26
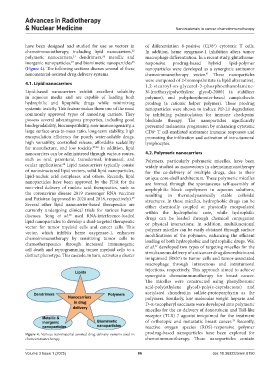
(Figure 4). The following sections discuss several of these nanoparticles were developed as a synergistic antitumor
nanomaterial-assisted drug delivery systems. chemoimmunotherapy vector. These nanoparticles
31
were composed of 2-bromopalmitate (a lipid alternative),
4.1. Lipid nanocarriers 1,2-stearoyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphoethanolamine-
Lipid-based nanocarriers exhibit excellent solubility N-[methoxy(polyethylene glycol)-2000] (a stabilizer
in aqueous media and are capable of loading both polymer), and polyphosphoester-based camptothecin
hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs while minimizing prodrug (a cationic helper polymer). These prodrug
systemic toxicity. This feature makes them one of the most nanoparticles were shown to induce PD-L1 degradation
commonly approved types of nanodrug carriers. They by inhibiting palmitoylation for immune checkpoint
possess several advantageous properties, including good blockade therapy. The nanoparticles significantly
biodegradability, biocompatibility, non-immunogenicity, a prevented melanoma progression by enhancing cytotoxic
large surface-area-to-mass ratio, long-term stability, high CD8 T cell-mediated antitumor immune responses and
+
encapsulation efficiency for poorly water-soluble drugs, promoting the infiltration and activation of intra-tumoral
high versatility, controlled release, affordable scalability lymphocytes.
for manufacture, and low toxicity. 27,28 In addition, lipid
nanocarriers can be administered through various routes, 4.2. Polymeric nanocarriers
such as oral, parenteral, transdermal, intranasal, and Polymers, particularly polymeric micelles, have been
ocular applications. Lipid nanocarriers typically consist widely studied as nanovectors in chemoimmunotherapy
28
of nanostructured lipid vectors, solid lipid nanoparticles, for the co-delivery of multiple drugs, due to their
lipid-nucleic acid complexes, and others. Recently, lipid unique core-shell architecture. These polymeric micelles
nanoparticles have been approved by the FDA for the are formed through the spontaneous self-assembly of
non-viral delivery of nucleic acid therapeutics, such as amphiphilic block copolymers in aqueous solutions,
the coronavirus disease 2019 messenger RNA vaccines resulting in thermodynamically stable colloidal
and Patisiran (approved in 2020 and 2018, respectively). structures. In these micelles, hydrophobic drugs can be
29
Several other lipid nanocarrier-based therapeutics are either chemically coupled or physically encapsulated
currently undergoing clinical trials for various human within the hydrophobic core, while hydrophilic
diseases. Yong et al. used RNA-interference-loaded drugs can be loaded through chemical conjugation
30
lipid nanoparticles to develop a dual-targeted therapeutic or physical interactions. In addition, multifunctional
vector for tumor myeloid cells and cancer cells. This polymer micelles can be easily obtained through surface
vector, which inhibits heme oxygenase-1, enhances modifications of the polymers, enhancing the efficient
chemoimmunotherapy by sensitizing tumor cells to loading of both hydrophobic and hydrophilic drugs. Wei
chemotherapeutics through increased immunogenic et al. developed two types of targeting micelles for the
32
cell death and reprogramming tumor myeloid cells to a simultaneous delivery of anticancer drug doxorubicin and
distinct phenotype. This cascade, in turn, activates a cluster
imiquimod (R837) to tumor cells and tumor-associated
macrophage through intravenous and intratumoral
injections, respectively. This approach aimed to achieve
synergistic chemoimmunotherapy for breast cancer.
The micelles were constructed using phenylboronic
acid-poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone) and
acetylated chondroitin sulfate-protoporphyrin as the
polymers. Similarly, low molecular weight heparin and
D-α-tocopheryl succinate were developed into polymeric
micelles for the co-delivery of doxorubicin and Toll-like
receptor (TLR) 7 agonist imiquimod for the treatment
of orthotopic and metastatic breast cancer. Recently,
33
reactive oxygen species (ROS)-responsive polymer
Figure 4. Various nanomaterial-assisted drug delivery systems used in prodrug-based nanoparticles have been explored for
chemoimmunotherapy chemoimmunotherapy. These nanoparticles contain
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 86 doi: 10.36922/arnm.8150