Page 91 - ARNM-3-1
P. 91
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Nanomaterials in cancer chemoimmunotherapy
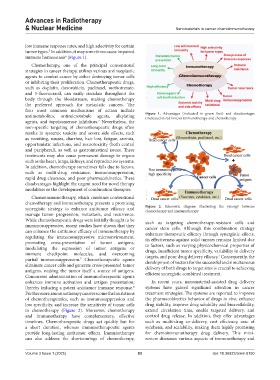
low immune response rates, and high selectivity for certain
tumor types. In addition, it may sometimes cause impaired
5
immune homeostasis (Figure 1).
6
Chemotherapy, one of the principal conventional
strategies in cancer therapy, utilizes various antineoplastic
agents to combat cancer by either destroying tumor cells
or inhibiting their proliferation. Chemotherapeutic drugs,
such as cisplatin, doxorubicin, paclitaxel, methotrexate,
and 5-fluorouracil, can easily circulate throughout the
body through the bloodstream, making chemotherapy
the preferred approach for metastatic cancers. The
four most common mechanisms of action include
antimetabolites, antimicrotubule agents, alkylating Figure 1. Advantages (indicated in green font) and disadvantages
(indicated in red font) of immunotherapy and chemotherapy
agents, and topoisomerase inhibitors. Nevertheless, the
7
non-specific targeting of chemotherapeutic drugs often
results in systemic toxicity and severe side effects, such
as vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, hair loss, fatigue, anemia,
opportunistic infections, and neurotoxicity (both central
and peripheral), as well as gastrointestinal issues. These
treatments may also cause permanent damage to organs
such as the heart, lungs, kidneys, and reproductive systems.
In addition, chemotherapy sometimes fails due to factors,
such as multi-drug resistance, immunosuppression,
rapid drug clearance, and poor pharmacokinetics. These
disadvantages highlight the urgent need for novel therapy
modalities or the development of combination therapies.
Chemoimmunotherapy, which combines conventional
chemotherapy and immunotherapy, presents a promising
synergistic strategy to enhance antitumor efficacy and Figure 2. Schematic diagram illustrating the synergy between
chemotherapy and immunotherapy
manage tumor progression, metastasis, and recurrence.
While chemotherapeutic drugs were initially thought to be such as targeting chemotherapy-resistant cells and
immunosuppressive, recent studies have shown that they cancer stem cells. Although this combination strategy
can enhance the antitumor efficacy of immunotherapy by enhances therapeutic efficacy through synergistic effects,
regulating the immunosuppressive microenvironment, its effectiveness against solid tumors remains limited due
promoting cross-presentation of tumor antigens, to factors, such as varying physicochemical properties of
modulating the expression of tumor antigens or drugs, insufficient tumor specificity, variability in delivery
immune checkpoint molecules, and overcoming targets, and poor drug delivery efficacy. Consequently, the
7
partial immunosuppression. Chemotherapeutic agents development of vectors for the successful and simultaneous
7
eliminate cancer cells and generate cross-presented tumor delivery of both drugs to target sites is crucial to achieving
antigens, making the tumor itself a source of antigens. efficient synergistic combined treatment.
Concurrent administration of immunotherapeutic agents
enhances immune activation and antigen presentation; In recent years, nanomaterial-assisted drug delivery
thereby inducing a potent antitumor immune response. systems have gained significant attention in cancer
8
Furthermore, immunotherapy can overcome the limitations treatment strategies. The systems are reported to improve
of chemotherapeutics, such as immunosuppression and the pharmacokinetics behavior of drugs in vivo, enhance
low specificity, and increase the sensitivity of tumor cells drug stability, improve drug solubility and bioavailability,
to chemotherapy (Figure 2). Moreover, chemotherapy extend circulation time, enable targeted delivery, and
and immunotherapy have complementary, effective control drug release. In addition, they offer advantages
timelines. Chemotherapeutic drugs act quickly but for such as multi-drug co-delivery, cost efficiency, ease of
a short duration, whereas immunotherapeutic agents synthesis, and scalability, making them highly promising
provide long-lasting antitumor effects. Immunotherapy for chemoimmunotherapy drug delivery. This mini-
can also address the shortcomings of chemotherapy, review discusses various aspects of immunotherapy and
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 83 doi: 10.36922/arnm.8150