Page 87 - ARNM-3-1
P. 87
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Cone beam-focused GK dosimetric analysis
A B
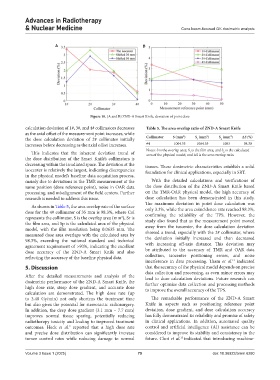
Figure 10. (A and B) ZND-A Smart Knife, deviation of point dose
calculation deviation of 1#, 3#, and 4# collimators decreases Table 5. The area overlap ratio of ZND‑A Smart Knife
as the axial offset of the measurement point increases, while 2 2 2
the dose calculation deviation of 2# collimator initially Collimator S (mm ) S (mm ) S (mm ) ∆S (%)
r
p
increases before decreasing as the axial offset increases. #4 1064.55 1064.55 1083 98.30
Notes: S is the overlap area; S is the film area; and S is the calculated
This indicates that the inherent deviation trend of area of the physical model; and ∆S is the area overlap ratio.
r
p
the dose distribution of the Smart Knife’s collimators is
decreasing within the irradiated space. The deviation at the tissues. These dosimetric characteristics establish a solid
isocenter is relatively the largest, indicating discrepancies foundation for clinical applications, especially in SRT.
in the physical model’s baseline data acquisition process,
mainly due to deviations in the TMR measurement at the With the detailed calculations and verifications of
same position (dose reference point), noise in OAR data the dose distribution of the ZND-A Smart Knife based
processing, and misalignment of the field centers. Further on the TMR-OAR physical model, the high accuracy of
research is needed to address this issue. dose calculation has been demonstrated in this study.
The maximum deviation in point dose calculation was
As shown in Table 5, the area overlap rate of the surface
dose for the 4# collimator of 35 mm is 98.3%, where Col only 3.3%, while the area coincidence rate reached 98.3%,
confirming the reliability of the TPS. However, the
represents the collimator, S is the overlap area (mm ), Sr is
2
the film area, and Sp is the calculated area of the physical study also found that as the measurement point moved
model, with the film resolution being 0.0635 mm. The away from the isocenter, the dose calculation deviation
measured dose area overlaps with the calculated area by showed a trend, especially with the 2# collimator, where
the deviation initially increased and then decreased
98.3%, exceeding the national standard and technical
agreement requirement of >90%, indicating the excellent with increasing off-axis distance. This deviation may
dose accuracy of the ZND-A Smart Knife and also be attributed to the accuracy of TMR and OAR data
reflecting the accuracy of the baseline physical data. collection, isocenter positioning errors, and noise
interference in data processing. Tham et al. indicated
12
5. Discussion that the accuracy of the physical model depends on precise
data collection and processing, as even minor errors may
After the detailed measurements and analysis of the lead to dose calculation deviations. Future research can
dosimetric performance of the ZND-A Smart Knife, the further optimize data collection and processing methods
high dose rate, steep dose gradient, and accurate dose to improve the overall accuracy of the TPS.
calculation are demonstrated. The high dose rate (up
to 3.48 Gy/min) not only shortens the treatment time The remarkable performance of the ZND-A Smart
but also gives the potential for stereotactic radiosurgery. Knife in aspects such as positioning reference point
In addition, the deep dose gradient (3.1 mm – 7.7 mm) deviation, dose gradient, and dose calculation accuracy
improves normal tissue sparing, potentially reducing has fully demonstrated its reliability and promise of safety
radiotherapy toxicity and leading to improved treatment in clinical applications. In addition, automated quality
outcomes. Heck et al. reported that a high dose rate control and artificial intelligence (AI) assistance can be
2
and precise dose distribution can significantly increase considered to improve its stability and consistency in the
tumor control rates while reducing damage to normal future. Choi et al. indicated that introducing machine-
13
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2025) 79 doi: 10.36922/arnm.6280