Page 61 - BH-2-1
P. 61
Brain & Heart Impact of ketogenic diet in adults with drug-resistant epilepsy
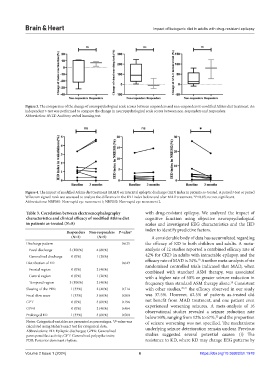
Figure 3. The comparison of the change of neuropsychological scale scores between responders and non-responders to modified Atkins diet treatment. An
independent t-test was performed to compare the change in neuropsychological scale scores between non-responders and responders.
Abbreviation: AVLT: Auditory verbal learning test.
Figure 4. The impact of modified Atkins diet treatment (MAD) on interictal epileptic discharge (IED) index in patients as-treated. A paired t-test or paired
Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to analyze the difference in the IED index before and after MAD treatment. *P<0.05; ns: not significant.
Abbreviations: NREM1: Non-rapid eye movement 1; NREM2: Non-rapid eye movement 2.
Table 3. Correlation between electroencephalography with drug-resistant epilepsy. We analyzed the impact of
characteristics and clinical efficacy of modified Atkins diet cognitive function using objective neuropsychological
in patients as‑treated (N=8) scales and investigated EEG characteristics and the IED
index to identify predictive factors.
Responders Non‑responders P‑value*
(N=3) (N=5) A considerable body of data has accumulated regarding
Discharge pattern 0.625 the efficacy of KD in both children and adults. A meta-
Focal discharge 3 (100%) 4 (80%) analysis of 12 studies reported a combined efficacy rate of
Generalized discharge 0 (0%) 1 (20%) 42% for CKD in adults with intractable epilepsy, and the
18
Distribution of ED 0.643 efficacy rate of MAD is 34%. Another meta-analysis of six
randomized controlled trials indicated that MAD, when
Frontal region 0 (0%) 2 (40%) combined with standard ASM therapy, was associated
Central region 0 (0%) 1 (20%) with a higher rate of 50% or greater seizure reduction in
Temporal region 3 (100%) 2 (40%) frequency than standard ASM therapy alone. Consistent
19
Slowing of the PDR 1 (33%) 2 (40%) 0.714 with other studies, 20,21 the efficacy observed in our study
Focal slow wave 1 (33%) 3 (60%) 0.500 was 37.5%. However, 62.5% of patients as-treated did
GPT 0 (0%) 3 (60%) 0.196 not benefit from MAD treatment, and one patient even
GPFA 0 (0%) 2 (40%) 0.464 experienced worsening seizures. A meta-analysis of 16
observational studies revealed a seizure reduction rate
Prolonged ED 1 (33%) 3 (60%) 0.500 below 50%, ranging from 12% to 67%, and the proportion
22
Notes: Categorical variables are presented as percentages. *P-value was of seizure worsening was not specified. The mechanisms
calculated using Fisher’s exact test for categorical data. underlying seizure deterioration remain unclear. Previous
Abbreviations: ED: Epileptic discharges; GPFA: Generalized
paroxysmal fast activity; GPT: Generalized polyspike train; studies suggested several potential causes: (i) The
PDR: Posterior dominant rhythm. resistance to KD, where KD may change EEG patterns by
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2024) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/bh.1978