Page 62 - BH-2-1
P. 62
Brain & Heart Impact of ketogenic diet in adults with drug-resistant epilepsy
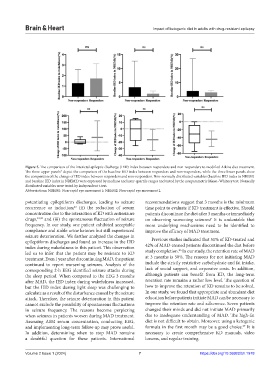
Figure 5. The comparison of the interictal epileptic discharge (IED) index between responders and non-responders to modified Atkins diet treatment.
The three upper panels* depict the comparison of the baseline IED index between responders and non-responders, while the three lower panels show
the comparison of the change of IED index between responders and non-responders. Non-normally distributed variables (baseline IED index in NREM1
and baseline IED index in NREM2) were expressed by medians and inter-quartile ranges and tested by the nonparametric Mann–Whitney test. Normally
distributed variables were tested by independent t-test.
Abbreviations: NREM1: Non-rapid eye movement 1; NREM2: Non-rapid eye movement 2.
potentiating epileptiform discharges, leading to seizure recommendations suggest that 3 months is the minimum
recurrence or induction; (ii) the reduction of serum time point to evaluate if KD treatment is effective. Should
23
concentration due to the interaction of KD with antiseizure patients discontinue the diet after 3 months or immediately
drugs, 24,25 and (iii) the spontaneous fluctuation of seizure on observing worsening seizures? It is undeniable that
frequency. In our study, one patient exhibited acceptable more underlying mechanisms need to be identified to
compliance and stable urine ketones but still experienced improve the efficacy of MAD treatment.
seizure deterioration. We further analyzed the changes in
epileptiform discharges and found an increase in the IED Previous studies indicated that 51% of KD-treated and
index during wakefulness in this patient. This observation 42% of MAD-treated patients discontinued the diet before
26
led us to infer that the patient may be resistant to KD study completion. In our study, the retention rate of MAD
treatment. Even 1 year after discontinuing MAD, the patient at 3 months is 50%. The reasons for not initiating MAD
continued to report worsening seizures. Analysis of the include the strictly restrictive carbohydrate and fat intake,
corresponding 2-h EEG identified seizure attacks during lack of social support, and expensive costs. In addition,
the sleep period. When compared to the EEG 3 months although patients can benefit from KD, the long-term
after MAD, the IED index during wakefulness increased, retention rate remains a rather low level. The question of
but the IED index during light sleep was challenging to how to improve the retention of KD remains to be solved.
calculate as a result of the disturbance caused by the seizure In our study, we found that appropriate and abundant diet
attack. Therefore, the seizure deterioration in this patient education before patients initiate MAD can be necessary to
cannot exclude the possibility of spontaneous fluctuations improve the retention rate and adherence. Seven patients
in seizure frequency. The reasons become perplexing changed their minds and did not initiate MAD primarily
when seizures in patients worsen during MAD treatment. due to inadequate understanding of MAD. The high-fat
Assessing ASM serum concentration, conducting EEG, diet is not difficult to obtain. Moreover, using a ketogenic
27
and implementing long-term follow-up may prove useful. formula in the first month may be a good choice. It is
In addition, determining when to stop MAD remains necessary to create comprehensive KD manuals, video
a doubtful question for these patients. International lessons, and regular training.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2024) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/bh.1978