Page 82 - BH-2-4
P. 82
Brain & Heart Automatic cardiac autonomic modulation assessment
A
B
C
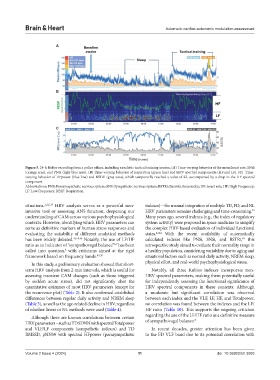
Figure 5. 24-h Holter recording from a police officer, including a realistic tactical training session. (A) Time-varying behavior of the mean heart rate, SNSi
(orange area), and PNSi (light blue area). (B) Time-varying behavior of respiration (green line) and HRV spectral components (HF and LF). (C) Time-
varying behavior of HFpower (blue line) and BSTRi (gray area), which temporarily reached a value of 82, accompanied by a drop in the HF spectral
component
Abbreviations: PNS: Parasympathetic nervous system; SNS: Sympathetic nervous system; BSTRi: Baevski stress index; HR: heart rate; HF: High Frequency;
LF: Low Frequency; RESP: Respiration.
situations. 1,2,5,35 HRV analysis serves as a powerful non- indexes) – the manual integration of multiple TD, FD, and NL
invasive tool or assessing ANS function, deepening our HRV parameters remains challenging and time-consuming.
44
understanding of CAM across various psychophysiological Many years ago, several indexes (e.g., the index of regulatory
contexts. However, identifying which HRV parameters can system activity) were proposed in space medicine to simplify
serve as definitive markers of human stress responses and the complex HRV-based evaluation of individual functional
evaluating the suitability of different analytical methods states. 43,44 With the recent availability of automatically
has been widely debated. 4,6-8,48 Notably, the use of LF/HF calculated indexes like PNSi, SNSi, and BSTRi, this
40
ratio as an indicator of “sympathovagal balance” has been retrospective study aimed to evaluate their normality range in
6,7
called into question, with criticisms aimed at the rigid a healthy population, considering variability due to aging and
8
framework based on frequency bands. 49,50 situational factors such as normal daily activity, NREM sleep,
In this study, a preliminary evaluation showed that short- physical effort, and real-world psychophysiological stress.
term HRV analysis from 2-min intervals, which is useful for Notably, all three Kubios indexes incorporate non-
assessing transient CAM changes (such as those triggered HRV spectral parameters, making them potentially useful
by sudden acute stress), did not significantly alter the for independently assessing the functional significance of
quantitative estimates of most HRV parameters (except for HRV spectral components in these contexts. Although
the recurrence plot) (Table 2). It also confirmed established a moderate but significant correlation was observed
differences between regular daily activity and NREM sleep between each index and the VLF, LF, HF, and Totalpower,
(Table 3), as well as the age-related decline in HRV, regardless no correlation was found between the indexes and the LF/
of whether linear or NL methods were used (Table 4). HF ratio (Table 10). This supports the ongoing criticism
Although there are known correlations between certain regarding the use of the LF/HF ratio as a definitive measure
HRV parameters – such as TD SDNN with spectral Totalpower of sympathovagal balance. 8
and VLF/LF components (sympathetic indexes) and TD In recent decades, greater attention has been given
RMSSD, pNN50 with spectral HFpower (parasympathetic to the FD VLF band due to its potential correlation with
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2024) 11 doi: 10.36922/bh.3503