Page 91 - BH-3-3
P. 91
Brain & Heart Combination of EDN and RDN treatment
A B A B
C D
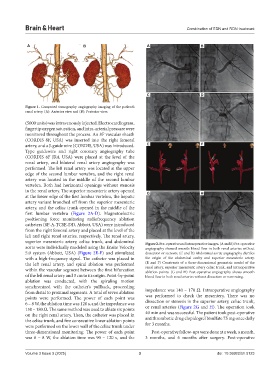
Figure 1. Computed tomography angiography imaging of the patient’s
renal artery. (A): Anterior view and (B): Posterior view.
(5000 units) was intravenously injected. Electrocardiogram,
fingertip oxygen saturation, and intra-arterial pressure were
monitored throughout the process. An 8F vascular sheath
(CORDIS 8F, USA) was inserted into the right femoral
artery, and a J-guide wire (CORDIS, USA) was introduced. E F
Type guidewire and right coronary angiography tube
(CORDIS 6F JR4, USA) were placed at the level of the
renal artery, and bilateral renal artery angiography was
performed. The left renal artery was located at the upper
edge of the second lumbar vertebra, and the right renal
artery was located in the middle of the second lumbar
vertebra. Both had horizontal openings without stenosis
in the renal artery. The superior mesenteric artery opened G H
at the lower edge of the first lumbar vertebra, the hepatic
artery variant branched off from the superior mesenteric
artery, and the celiac trunk opened in the middle of the
first lumbar vertebra (Figure 2A-D). Magnetoelectric
positioning force monitoring radiofrequency ablation
catheters (8F-A-TCSE-DD, Abbott, USA) were introduced
from the right femoral artery and placed at the level of the
left and right renal arteries, respectively. The renal artery,
superior mesenteric artery, celiac trunk, and abdominal Figure 2. Pre-operative and intraoperative images. (A and B) Pre-operative
aorta were individually modeled using the Ensite Velocity angiography showed smooth blood flow in both renal arteries without
5.0 system (Abbott, USA) (Figure 2E-F) and stimulated dissection or stenosis. (C and D) Abdominal aortic angiography clarifies
with a high-frequency signal. The catheter was placed in the origin of the abdominal cavity and superior mesenteric artery.
the left renal artery, and spiral ablation was performed (E and F) Constructs of a three-dimensional geometric model of the
within the vascular segment between the first bifurcation renal artery, superior mesenteric artery celiac trunk, and intraoperative
ablation points. (G and H) Post-operative angiography shows smooth
of the left renal artery and 3 cm to its origin. Point-by-point blood flow in both renal arteries without dissection or narrowing.
ablation was conducted, with the spiraling motion
synchronized with the catheter’s pullback, proceeding
from distal to proximal segments. A total of seven ablation impedance was 140 – 170 Ω. Intraoperative angiography
points were performed. The power of each point was was performed to check the mesentery. There was no
6 – 8 W, the ablation time was 120 s, and the impedance was dissection or stenosis in the superior artery, celiac trunk,
150 – 180 Ω. The same method was used to ablate six points or renal arteries (Figure 2G and H). The operation took
on the right renal artery. Then, the catheter was placed in 40 min and was successful. The patient took post-operative
the celiac trunk, and five consecutive linear ablation points antithrombotic drug clopidogrel bisulfate 75 mg once daily
were performed on the lower wall of the celiac trunk under for 3 months.
three-dimensional monitoring. The power of each point Post-operative follow-ups were done at a week, a month,
was 6 – 8 W, the ablation time was 90 – 120 s, and the 3 months, and 6 months after surgery. Post-operative
Volume 3 Issue 3 (2025) 3 doi: 10.36922/bh.5123