Page 21 - EER-2-2
P. 21
Explora: Environment
and Resource Trace elements in Mediterranean mussels
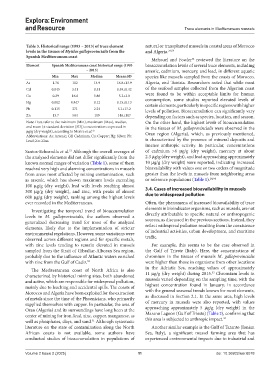
Table 3. Historical range (1993 – 2013) of trace element natural or transplanted mussels in coastal areas of Morocco
levels in the tissues of Mytilus galloprovincialis from the and Algeria. 24,54
Spanish Mediterranean coast
Mehouel and Fowler reviewed the literature on the
54
Element Spanish Mediterranean coast historical range (1993 bioaccumulation levels of several trace elements, including
– 2013) arsenic, cadmium, mercury, and lead, in different aquatic
Min Max Median Mean±SD species like mussels sampled from the coasts of Morocco,
As 1.76 112 14.9 16.8±13.9 Algeria, and Tunisia. Researchers noted that while most
Cd 0.045 3.41 0.51 0.59±0.42 of the seafood samples collected from the Algerian coast
Cu 0.29 16.6 5.86 5.3±3.0 were found to be within acceptable limits for human
Hg 0.002 0.847 0.12 0.15±0.13 consumption, some studies reported elevated levels of
certain elements, particularly in specific regions with higher
Pb 0.115 271 2.24 5.1±17.2 levels of pollution. Bioaccumulation can significantly vary
Zn 13.7 584 119 146±107 depending on factors such as species, location, and season.
Note: Data refer to the minimum (Min), maximum (Max), median, On the other hand, the highest levels of bioaccumulation
and mean (± standard deviation [SD]) concentrations expressed in in the tissues of M. galloprovincialis were observed in the
µg/g (dry weight), according to Mestre et al. 52 Oran region (Algeria), which, as previously mentioned,
Abbreviations: As: Arsenic; Cd: Cadmium; Cu: Copper; Hg: Silver; Pb:
Lead; Zn: Zinc. is characterized by the presence of mineral deposits and
intense anthropic activity. In particular, concentrations
Santos-Echeandía et al. Although the overall averages of of cadmium >6 µg/g (dry weight), mercury at about
53
the analyzed elements did not differ significantly from the 2.3 µg/g (dry weight), and lead approaching approximately
known normal ranges of variation (Table 1), some of them 10 µg/g (dry weight) were reported, indicating increased
reached very high and alarming concentrations in mussels bioavailability with values one or two orders of magnitude
from areas most affected by mining contamination, such greater than the levels in mussels from neighboring areas
as arsenic, which has shown maximum levels exceeding or reference populations (Table 1). 24,54
100 µg/g (dry weight), lead with levels reaching almost
300 µg/g (dry weight), and zinc, with peaks of almost 3.4. Cases of increased bioavailability in mussels
600 µg/g (dry weight), ranking among the highest levels due to widespread pollution
ever recorded in the Mediterranean. Often, the phenomena of increased bioavailability of trace
Investigating the temporal trend of bioaccumulation elements in bioindicator organisms, such as mussels, are not
levels in M. galloprovincialis, the authors observed a directly attributable to specific natural or anthropogenic
generalized decreasing trend for most of the analyzed sources, as discussed in the previous sections. Instead, they
reflect widespread pollution resulting from the coexistence
elements, likely due to the implementation of stricter
environmental regulations. However, some variations were of industrial activities, urban development, and maritime
observed across different regions and for specific metals, traffic.
with zinc levels tending to remain elevated in mussels For example, this seems to be the case observed in
sampled from the Strait of Gibraltar-Alboran Sea region, the Gulf of Trieste (Italy). Here, the concentrations of
probably due to the influence of Atlantic waters enriched chromium in the tissues of mussels M. galloprovincialis
with zinc from the Gulf of Cadiz. 53 were higher than those in organisms from other locations
in the Adriatic Sea, reaching values of approximately
The Mediterranean coast of North Africa is also 53
characterized by historical mining sites, both abandoned 11 µg/g (dry weight) during 2015. Chromium levels in
and active, which are responsible for widespread pollution, mussels varied depending on the sampling time, with the
mainly due to leaching and accidental spills. The coasts of highest concentration found in January, in accordance
Morocco and Algeria have been exploited for the extraction with the general seasonal trends known for most elements,
of metals since the time of the Phoenicians, who primarily as discussed in Section 2.1. In the same area, high levels
supplied themselves with copper. In particular, the area of of mercury in mussels were also reported, with values
Oran (Algeria) and its surroundings have long been at the approaching approximately 5 µg/g (dry weight) in the
center of mining for iron, lead, zinc, copper, manganese, as Marano Lagoon (Gulf of Trieste) (Table 2), confirming that
44
51
well as phosphates, clays, and sand. Although systematic this area is subjected to anthropic impact.
literature on the state of contamination along the North Another similar example is the Gulf of Taranto (Ionian
African coasts is not available, some authors have Sea, Italy), a significant mussel farming area that has
conducted studies of bioaccumulation in populations of experienced environmental impacts due to industrial and
Volume 2 Issue 2 (2025) 11 doi: 10.36922/eer.8078