Page 116 - EER-2-3
P. 116
Explora: Environment
and Resource Enzymatic degradation
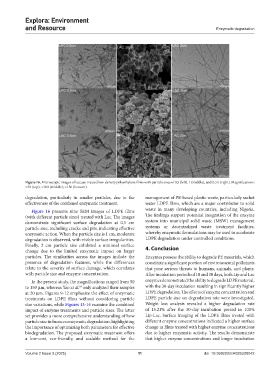
Figure 16. Microscopic images of laccase-treated low-density polyethylene films with particle sizes of 0.5 (left), 1 (middle), and 2 cm (right). Magnifications:
×50 (top); ×100 (middle); ×150 (bottom).
degradation, particularly in smaller particles, due to the management of PE-based plastic waste, particularly sachet
effectiveness of the combined enzymatic treatment. water LDPE films, which are a major contributor to solid
Figure 16 presents nine SEM images of LDPE films waste in many developing countries, including Nigeria.
(with different particle sizes) treated with Lac. The images The findings support potential integration of the enzyme
demonstrate significant surface degradation at 0.5 cm system into municipal solid waste (MSW) management
particle size, including cracks and pits, indicating effective systems or decentralized waste treatment facilities,
enzymatic action. When the particle size is 1 cm, moderate whereby enzymatic formulations may be used to accelerate
degradation is observed, with visible surface irregularities. LDPE degradation under controlled conditions.
Finally, 2 cm particle size exhibited a minimal surface 4. Conclusion
change due to the limited enzymatic impact on larger
particles. The similarities across the images include the Enzymes possess the ability to degrade PE materials, which
presence of degradation features, while the differences constitute a significant portion of environmental pollutants
relate to the severity of surface damage, which correlates that pose serious threats to humans, animals, and plants.
with particle size and enzyme concentration. After incubation periods of 10 and 30 days, both Lip and Lac
In the present study, the magnifications ranged from 50 enzymes demonstrated the ability to degrade LDPE material,
to 150 µm, whereas Yao et al. only analyzed their samples with the 30-day incubation resulting in significantly higher
59
at 20 µm. Figures 9-12 emphasize the effect of enzymatic LDPE degradation. The effects of enzyme concentration and
treatments on LDPE films without considering particle LDPE particle size on degradation rate were investigated.
size variations, while Figures 13-16 examine the combined Weight loss analysis revealed a higher degradation rate
impact of enzyme treatments and particle sizes. The latter of 15.21% after the 30-day incubation period in 100%
set provides a more comprehensive understanding of how Lip-Lac. Surface imaging of the LDPE films treated with
particle size influences enzymatic degradation, highlighting different enzyme concentrations indicated a higher surface
the importance of optimizing both parameters for effective change in films treated with higher enzyme concentrations
biodegradation. The proposed enzymatic treatment offers due to higher enzymatic activity. The results demonstrate
a low-cost, eco-friendly, and scalable method for the that higher enzyme concentrations and longer incubation
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 11 doi: 10.36922/EER025220042