Page 19 - EER-2-3
P. 19
Explora: Environment
and Resource Environmental contamination of titanium
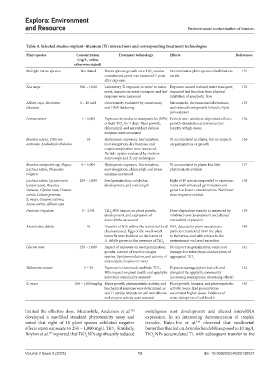
Table 4. Selected studies onplant–titanium (Ti) interactions and corresponding treatment technologies
Plant species Concentration Treatment technology Effects References
(mg/L, unless
otherwise stated)
Multiple native species Not stated Native species growth on a TiO residue Normal native plant species rehabilitation 131
2
containment pond was measured 5 years on site
after exposure
Zea mays 300 – 1,000 Laboratory Ti exposure in water to maize Exposure caused reduced water transport; 132
roots; impacts on water transport and leaf impacted leaf function from physical
response were measured inhibition of apoplastic flow
Allium cepa, Nicotiana 0 – 10 mM Genotoxicity evaluated by comet assay Micronuclei, chromosomal aberrations, 133
tabacum and DNA laddering and reduced root growth linked to lipid
peroxidation
Lemna minor 1 – 2,000 Exposure in media to nanoparticles (NPs) Particle size- and dose-dependent effects; 134
or bulk TiO for 7 days. Plant growth, growth stimulation at low doses but
2
chlorophyll, and antioxidant defense toxicity at high doses
enzymes were measured
Brassica napus, Triticum 10 Hydroponic exposure. Germination, Ti accumulated in planta, but no impacts 136
aestivum, Arabidopsis thaliana root elongation, dry biomass, and on germination or growth
evapotranspiration were measured.
Particle uptake evaluated by electron
microscopy and X-ray techniques
Brassica campestris ssp. Napus, 0 – 5,000 Hydroponic exposure. Germination, Ti accumulated in plants but little 137
Lactuca sativa, Phaseolus root elongation, chlorophyll and stress phytotoxicity evident
vulgaris enzymes measured
Lactuca sativa, Lycopersicon 250 – 1,000 Seed germination, cotyledon Eight of 10 species responded to exposure; 138
lycopersicum, Brassica development, and root length many with enhanced germination and
oleracea, Glycine max, Daucus growth at lower concentrations. Nonlinear
carota, Lolium perenne, dose-response evident
Z. mays, Cucumis sativus,
Avena sativa, Allium cepa
Panicum virgatum 0 – 2.5% TiO NPs’ impact on plant growth, Dose-dependent toxicity as measured by 139
2
development, and expression of inhibited root development and altered
microRNAs measured microRNA expression
Aristolochia debilis 10 Transfer of NPs within the terrestrial food TiO detected in plant vasculature; 140
2
chain assessed. Eggs of the swallowtail particles transferred from the plant
butterfly were hatched on the leaves of to the larvae, and with release to the
A. debilis grown in the presence of TiO 2 environment via larval excretion
Glycine max 250 – 1,000 Impact of exposure on seed germination, No impact on germination; some root 141
growth, content of reactive oxygen damage due tothe physical adsorption of
species, lipid peroxidation, and activity of aggregated TiO 2
antioxidant enzymes in roots
Vallisneria natans 5 – 20 Exposure to nanoscale and bulk TiO₂ Exposure damaged plant leaf cells and 142
NPs; impact on plant health and epiphytic disrupted the epiphytic community
microbial community assessed (increasing some groups, decreasing others)
Z. mays 100 – 1,000 mg/kg Maize growth, photosynthetic activity, and Plant growth, biomass, and photosynthetic 143
biochemical response were determined, as activity. Some lipid peroxidation
was Ti uptake. Impacts on soil microbiome occurredat higher doses. Evidence of
and enzyme activity were assessed some disruption of soil health
limited the effective dose. Meanwhile, Andersen et al. switchgrass root development and altered microRNA
138
developed a modified standard phytotoxicity assay and expression. In an interesting demonstration of trophic
noted that eight of 10 plant species exhibited negative transfer, Kubo-Irie et al. observed that swallowtail
140
effects upon exposure to 250 – 1,000 mg/L TiO . Similarly, butterflies that fed on Aristolochia debilisexposed to 10 mg/L
2
Boykov et al. reported that TiO NPs significantly reduced TiO NPs accumulated Ti, with subsequent transfer to the
139
2
2
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 13 doi: 10.36922/EER025130027