Page 20 - EER-2-3
P. 20
Explora: Environment
and Resource Environmental contamination of titanium
environment from excretion. More recently, de Melo et al. TiO NPsled to significant root tissue damage, largely
141
2
observed that exposure of soybean to 250 – 1,000 mg/L through particle adsorption and direct physical interaction.
Similarly, Alklaf et al. reported that exposure of the
142
aquatic plant Vallisneria natans to 5 – 20 mg/L anatase for
30 days resulted in damaged leaf cells, altered epiphytic
species composition, and reduced interaction intensity
among the epiphytic genera in the microbiome. Bakshi and
Kumar reported that exposure of corn grown in soil to
143
TiO NPs at concentrations of 100 – 1,000 mg/kg had little
2
impact on growth or photosynthesis. However, oxidative
stress and Ti uptake were observed at the high dose range.
Similar observations were reported for green pea (Pisum
sativum L.) at 10 – 100 mg/L TiO NPs. 144
2
5. Risk management of Ti in the
contaminated environment
5.1. Remediation of Ti-contaminated soil
The investigation of Ti removal from the environment
is limited due to the generally perceived low biological
toxicity of the element. However, with the escalating
145
utilization of Ti-containing products and the emergence
of negative incidents, such as the European Food Safety
Authority (EFSA)’s prohibition on the use of nano/micro
Figure 2. Schematic highlighting the overall beneficial effects on plants TiO in food and the genotoxicity of TiO indicated by
exposed to TiO nanoparticles. Created with BioRender.com. Zuverza- 2 146,147 2
2
Mena, N. and White, J. (2025) https://BioRender.com/lwvj7lx. meta-analyses, it has become imperative to regulate
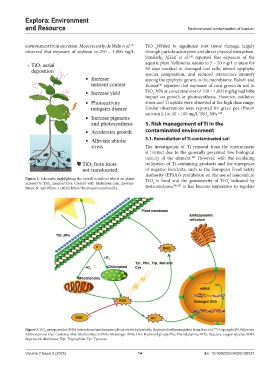
Figure 3. TiO nanoparticles (NPs) interactions/mechanisms of toxicity with plant cells. Reprinted with permission from Hou et al. ; Copyright 2019 Elsevier.
135
2
Abbreviations: Cys: Cysteine; Met: Methionine; mRNA: Messenger RNA; OH: Hydroxyl group; Phe: Phenylalanine; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; SOD:
Superoxide dismutase; Trp: Tryptophan; Tyr: Tyrosine.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 14 doi: 10.36922/EER025130027