Page 46 - EER-2-3
P. 46
Explora: Environment
and Resource Maize–pigeon pea intercropping in Ghana
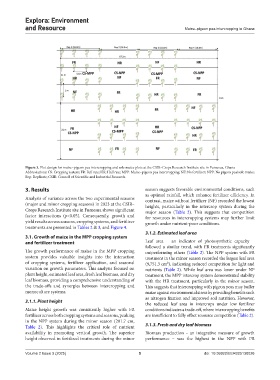
Figure 3. Plot design for maize–pigeon pea intercropping and sole maize plots at the CSIR–Crops Research Institute site in Fumesua, Ghana
Abbreviations: CS: Cropping system; FR: Full rate; HR: Half rate; MPP: Maize–pigeon pea intercropping; NF: No fertilizer; NPP: No pigeon pea/sole maize;
Rep: Replicate; CSIR: Council of Scientific and Industrial Research.
3. Results season suggests favorable environmental conditions, such
as optimal rainfall, which enhance fertilizer efficiency. In
Analysis of variance across the two experimental seasons contrast, maize without fertilizer (NF) recorded the lowest
(major and minor cropping seasons) in 2023 at the CSIR– heights, particularly in the intercrop system during the
Crops Research Institute site in Fumesua shows significant major season (Table 2). This suggests that competition
factor interactions (p<0.05). Consequently, growth and for resources in intercropping systems may further limit
yield results across seasons, cropping systems, and fertilizer growth under nutrient-poor conditions.
treatments are presented in Tables 2 & 3, and Figure 4.
3.1.2. Estimated leaf area
3.1. Growth of maize in the MPP cropping system
and fertilizer treatment Leaf area – an indicator of photosynthetic capacity –
followed a similar trend, with FR treatments significantly
The growth performance of maize in the MPP cropping outperforming others (Table 2). The NPP system with FR
system provides valuable insights into the interaction treatment in the minor season recorded the largest leaf area
of cropping systems, fertilizer application, and seasonal (9,751.3 cm²), indicating reduced competition for light and
variation on growth parameters. This analysis focused on nutrients (Table 2). While leaf area was lower under NF
plant height, estimated leaf area, fresh leaf biomass, and dry treatment, the MPP intercrop system demonstrated stability
leaf biomass, providing a comprehensive understanding of with the HR treatment, particularly in the minor season.
the trade-offs and synergies between intercropping and This suggests that intercropping with pigeon peas may buffer
monoculture systems. maize against environmental stress by providing benefits such
as nitrogen fixation and improved soil nutrition. However,
3.1.1. Plant height the reduced leaf area in intercrops under low fertilizer
Maize height growth was consistently higher with FR conditions indicates a trade-off, where intercropping benefits
fertilizer across both cropping systems and seasons, peaking are insufficient to fully offset resource competition (Table 2).
in the NPP system during the minor season (201.7 cm,
Table 2). This highlights the critical role of nutrient 3.1.3. Fresh and dry leaf biomass
availability in promoting vertical growth. The superior Biomass production – an integrative measure of growth
height observed in fertilized treatments during the minor performance – was the highest in the NPP with FR
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/EER025130026