Page 110 - EJMO-9-1
P. 110
Eurasian Journal of Medicine and
Oncology
Genomics of breast cancer in Western Kazakhstan
(controls). We identified 28 statistically significant
polymorphisms associated with the risk of developing BC,
seven of which were previously included in the GWAS
catalog: RARG (Rs2229774), FGFR2 (Rs2981582), ATM
(Rs1800057), MAP3K1 (Rs889312), BRCA2 (Rs11571833),
FGFR2 (Rs7895676), and FGFR2 (Rs1219648). Table 11
presents the key characteristics of these 28 polymorphisms,
which are associated with BC risk in women from the
Aktobe region.
The case–control study design provides a framework
for comparing the relationship between BC risk and
individual polymorphisms with existing literature on the
genetic contribution to BC development. Bioinformatics
analysis is important for determining the specific effects
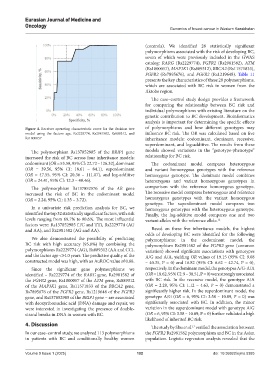
Figure 4. Receiver operating characteristic curve for the decision tree of polymorphisms and how different genotypes may
model using the factors age, Rs2229774, Rs2981582, Rs889312, and influence BC risk. The OR was calculated based on five
Rs1800057 inheritance models: codominant, dominant, recessive,
superdominant, and log-additive. The results from these
The polymorphism Rs137852985 of the BRIP1 gene models showed variations in the “genotype-phenotype”
increased the risk of BC across four inheritance models: relationship for BC risk.
codominant (OR = 53.58, 95% CI: 22.72 – 126.32), dominant The codominant model compares heterozygous
(OR = 39.56, 95% CI: 18.61 – 84.1), superdominant and variant homozygous genotypes with the reference
(OR = 47.55, 95% CI: 20.36 – 111.07), and log-additive homozygous genotype. The dominant model combines
(OR = 24.41, 95% CI: 12.3 – 48.46). heterozygous and variant homozygous genotypes in
The polymorphism Rs137852576 of the AR gene comparison with the reference homozygous genotype.
increased the risk of BC in the codominant model The recessive model compares heterozygous and reference
(OR = 2.24, 95% CI: 1.35 – 3.72). homozygous genotypes with the variant homozygous
genotype. The superdominant model compares two
In a univariate risk prediction analysis for BC, we homozygous genotypes with the heterozygous genotype.
identified the top 32 statistically significant factors, with risk Finally, the log-additive model compares one and two
levels ranging from 69.7% to 90.6%. The most influential variant alleles with the reference allele. 12
factors were: Rs137852985 (TC and TT), Rs2229774 (AG
and AA), and Rs2981582 (AG and AA). Based on these five inheritance models, the highest
odds of developing BC were identified for the following
We also demonstrated the possibility of predicting polymorphisms: in the codominant model, the
BC risk with high accuracy (95.8%) by combining the polymorphism Rs2981582 of the FGFR2 gene (common
polymorphisms Rs2229774 (AG), Rs889312 (AA and CC), variation) showed significant associations with genotypes
and the factor age <54.0 years. The predictive quality of the A/G and A/A, yielding OR values of 19.15 (95% CI: 9.08
constructed model was high, with an AuROC value of 0.88. – 40.35, P = 0) and 16.82 (95% CI: 6.62 – 42.74, P = 0),
Since the significant gene polymorphisms we respectively. In the dominant model, the genotypes A/G-A/A
identified – Rs2229774 of the RARG gene, Rs2981582 of (OR = 18.62, 95% CI: 9 – 38.51, P = 0) were strongly associated
the FGFR2 gene, Rs1800057 of the ATM gene, Rs889312 with BC risk. In the recessive model, the genotype A/A
of the MAP3K1 gene, Rs11571833 of the BRCA2 gene, (OR = 2.28, 95% CI: 1.12 – 4.63, P = 0) demonstrated a
Rs7895676 of the FGFR2 gene, Rs1219648 of the FGFR2 significantly higher risk. In the superdominant model, the
gene, and Rs137852985 of the BRIP1 gene – are associated genotype A/G (OR = 6, 95% CI: 3.58 – 10.09, P = 0) was
with deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) damage and repair, we significantly associated with BC. In addition, the minor
were interested in investigating the presence of double- variation in the superdominant model with genotype A/G
strand breaks in DNA in women with BC. (OR = 6, 95% CI: 3.58 – 10.09, P = 0) further validated a high
likelihood of inherited BC risk.
4. Discussion The study by Shu et al. verified the association between
13
In our case–control study, we analyzed 113 polymorphisms the FGFR2 Rs2981582 polymorphism and BC in the Asian
in patients with BC and conditionally healthy women population. Logistic regression analysis revealed that the
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2025) 102 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.5385