Page 109 - EJMO-9-1
P. 109
Eurasian Journal of Medicine and
Oncology
Genomics of breast cancer in Western Kazakhstan
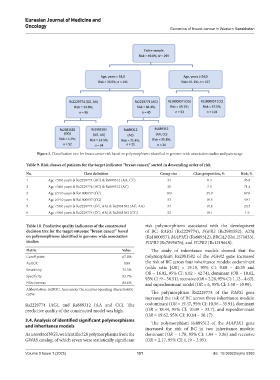
Figure 3. Classification tree for breast cancer risk based on polymorphisms identified in genome-wide association studies and patient age
Table 9. Risk classes of patients for the target indicator “breast cancer,” sorted in descending order of risk
No. Class definition Group size Class proportion, % Risk, %
1 Age <54.0 years & Rs2229774 (AG) & Rs889312 (AA, CC) 24 8.4 95.8
2 Age <54.0 years & Rs2229774 (AG) & Rs889312 (AC) 21 7.3 71.4
3 Age ≥54.0 years & Rs1800057 (CC) 103 35.9 67.0
4 Age ≥54.0 years & Rs1800057 (CG) 53 18.5 49.1
5 Age <54.0 years & Rs2229774 (GG, AA) & Rs2981582 (AG, AA) 34 11.8 23.5
6 Age <54.0 years & Rs2229774 (GG, AA) & Rs2981582 (GG) 52 18.1 1.9
Table 10. Predictive quality indicators of the constructed risk polymorphisms associated with the development
decision tree for the target outcome “breast cancer” based of BC: RARG (Rs2229774), FGFR2 (Rs2981582), ATM
on polymorphisms identified in genome‑wide association (Rs1800057), MAP3K1 (Rs889312), BRCA2 (Rs11571833),
studies FGFR2 (Rs7895676), and FGFR2 (Rs1219648).
Metric Value The study of inheritance models showed that the
Cutoff point 67.0% polymorphism Rs2981582 of the FGFR2 gene increased
AuROC 0.88 the risk of BC across four inheritance models: codominant
Sensitivity 75.5% (odds ratio [OR] = 19.15, 95% CI: 9.08 – 40.35 and
OR = 16.82, 95% CI: 6.62 – 42.74), dominant (OR = 18.62,
Specificity 93.7% 95% CI: 9 – 38.51), recessive (OR = 2.28, 95% CI: 1.12 – 4.63),
Effectiveness 84.6% and superdominant model (OR = 6, 95% CI: 3.58 – 10.09).
Abbreviation: AuROC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic
curve. The polymorphism Rs2229774 of the RARG gene
increased the risk of BC across three inheritance models:
Rs2229774 (AG), and Rs889312 (AA and CC). The codominant (OR = 19.47, 95% CI: 10.56 – 35.91), dominant
predictive quality of the constructed model was high. (OR = 18.44, 95% CI: 10.09 – 33.7), and superdominant
(OR = 19.62, 95% CI: 10.64 – 36.17).
3.4. Analysis of identified significant polymorphisms The polymorphism Rs889312 of the MAP3K1 gene
and inheritance models
increased the risk of BC in two inheritance models:
As a result of NGS, we identified 28 polymorphisms from the dominant (OR = 1.78, 95% CI: 1.04 – 3.06) and recessive
GWAS catalog, of which seven were statistically significant (OR = 2.17, 95% CI: 1.19 – 3.95).
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2025) 101 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.5385