Page 12 - EJMO-9-1
P. 12
Eurasian Journal of Medicine and
Oncology
Single-cell RNA-seq in malignant skin tumors
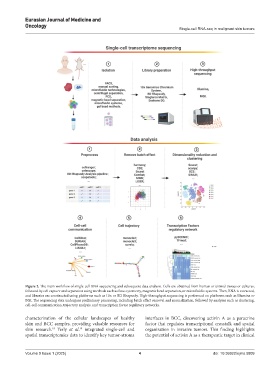
Figure 2. The main workflow of single-cell RNA sequencing and subsequent data analysis. Cells are obtained from human or animal tissues or cultures,
followed by cell capture and separation using methods such as flow cytometry, magnetic bead separation, or microfluidic systems. Then, RNA is extracted,
and libraries are constructed using platforms such as 10× or BD Rhapsody. High-throughput sequencing is performed on platforms such as Illumina or
BGI. The sequencing data undergoes preliminary processing, including batch effect removal and normalization, followed by analyses such as clustering,
cell-cell communication, trajectory analysis, and transcription factor regulatory networks.
characterization of the cellular landscapes of healthy interfaces in BCC, discovering activin A as a paracrine
skin and BCC samples, providing valuable resources for factor that regulates transcriptional crosstalk and spatial
skin research. Yerly et al. integrated single-cell and organization in invasive tumors. This finding highlights
18
19
spatial transcriptomics data to identify key tumor-stroma the potential of activin A as a therapeutic target in clinical
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2025) 4 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.5809