Page 162 - EJMO-9-2
P. 162
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology Genetic insights into CAD drug targets
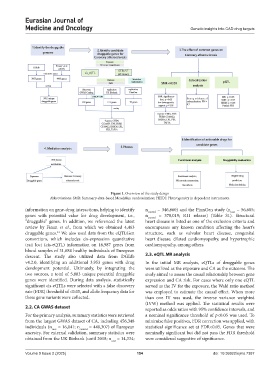
Figure 1. Overview of the study design
Abbreviations: SMR: Summary-data-based Mendelian randomization; HEIDI: Heterogeneity in dependent instruments.
information on gene-drug interactions, helping to identify n control = 346,860) and the FinnGen study (n = 56,685;
case
genes with potential value for drug development, i.e., n control = 378,019; R11 release) (Table S1). Structural
“druggable” genes. In addition, we referenced the latest heart disease is listed as one of the exclusion criteria and
review by Finan et al., from which we obtained 4,463 encompasses any known condition affecting the heart’s
13
druggable genes. We also used data from the eQTLGen structure, such as valvular heart disease, congenital
consortium, which includes cis-expression quantitative heart disease, dilated cardiomyopathy, and hypertrophic
trait loci (cis-eQTL) information on 16,987 genes from cardiomyopathy, among others.
blood samples of 31,684 healthy individuals of European
descent. The study also utilized data from DGIdb 2.3. eQTL MR analysis
v4.2.0, identifying an additional 3,953 genes with drug In the initial MR analysis, eQTLs of druggable genes
development potential. Ultimately, by integrating the were utilized as the exposure and CA as the outcome. The
two sources, a total of 5,883 unique potential druggable study aimed to assess the causal relationship between gene
genes were identified. During data analysis, statistically expression and CA risk. For cases where only one eQTL
significant cis-eQTLs were selected with a false discovery served as the IV for the exposure, the Wald ratio method
rate (FDR) threshold of <0.05, and allele frequency data for was employed to estimate the causal effect. When more
these gene variants were collected. than one IV was used, the inverse variance weighted
(IVW) method was applied. The statistical results were
2.2. CA GWAS dataset reported as odds ratios with 95% confidence intervals, and
For the primary analysis, summary statistics were retrieved a nominal significance threshold of p<0.05 was used. To
from the largest GWAS dataset of CA, including 456,348 minimize false positives, FDR correction was applied, with
individuals (n = 16,041; n control = 440,307) of European statistical significance set at FDR<0.05. Genes that were
case
ancestry. For external validation, summary statistics were nominally significant but did not pass the FDR threshold
obtained from the UK Biobank (until 2018; n = 14,334; were considered suggestive of significance.
case
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2025) 154 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.7387