Page 170 - EJMO-9-2
P. 170
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology Genetic insights into CAD drug targets
A D
B E
C F
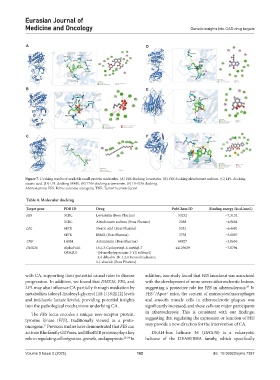
Figure 7. Docking results of available small protein molecules. (A) FES docking Lovastatin. (B) FES docking alendronate sodium. (C) LPL docking
stearic acid. (D) LPL docking IBMX. (E) TNF docking artemisinin. (F) DHX36 docking.
Abbreviations: FES: Feline sarcoma oncogene; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
Table 4. Molecular docking
Target gene PDB ID Drug PubChem ID Binding energy (kcaL/moL)
FES 3CBL Lovastatin (Boss Pharma) 53232 −7.3132
3CBL Alendronate sodium (Boss Pharma) 2088 −4.9684
LPL 6E7K Stearic acid (Boss Pharma) 5281 −6.4691
6E7K IBMX (Boss Pharma) 3758 −5.6087
TNF 1A8M Artemisinin (Boss Pharma) 68827 −5.0636
DHX36 AlphaFold: (3s)-3-Cyclopentyl-6-methyl-7 44129629 −7.0794
Q9H2U1 -[(4-methylpiperazin-1-Yl) sulfonyl]
-3,4-dihydro-2h-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine
1,1-dioxide (Boss Pharma)
with CA, supporting their potential causal roles in disease addition, one study found that FES knockout was associated
progression. In addition, we found that DHX36, FES, and with the development of more severe atherosclerotic lesions,
25
LPL may also influence CA partially through mediation by suggesting a protective role for FES in atherosclerosis. In
metabolites (oleoyl-linoleoyl-glycerol [18:1/18:2] [2] levels FES /Apoe mice, the content of monocytes/macrophages
-/-
-/-
and imidazole lactate levels), providing potential insights and smooth muscle cells in atherosclerotic plaques was
into the pathological mechanisms underlying CA. significantly increased, and these cells are major participants
The FES locus encodes a unique non-receptor protein, in atherosclerosis. This is consistent with our findings,
tyrosine kinase (FES), traditionally viewed as a proto- suggesting that regulating the expression or function of FES
oncogene. Previous studies have demonstrated that FES can may provide a new direction for the intervention of CA.
21
activate Rho family GTPases, and RhoBTB proteins play a key DEAH-box helicase 36 (DHX36) is a eukaryotic
role in regulating cell migration, growth, and apoptosis. 22-24 In helicase of the DEAH/RHA family, which specifically
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2025) 162 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.7387