Page 216 - EJMO-9-2
P. 216
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology Tetramethyl thyroxine boosts bladder cancer
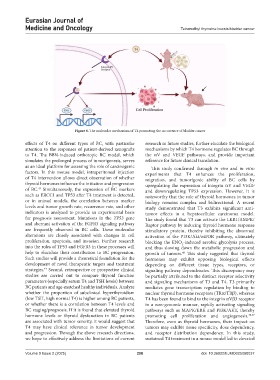
Figure 6. The molecular mechanism of T4 promoting the occurrence of bladder cancer
effects of T4 on different types of BC, with particular research in future studies, further elucidate the biological
attention to the responses of patient-derived xenografts mechanisms by which T4 hormone regulates BC through
to T4. The BBN-induced orthotopic BC model, which the αV and VEGF pathways, and provide important
simulates the prolonged process of tumorigenesis, serves reference for future clinical translation.
as an ideal platform for assessing the role of carcinogenic This study confirmed through in vivo and in vitro
factors. In this mouse model, intraperitoneal injection experiments that T4 enhances the proliferation,
of T4 intervention allows direct observation of whether migration, and tumorigenic ability of BC cells by
thyroid hormones influence the initiation and progression upregulating the expression of integrin αV and VEGF
43
of BC. Simultaneously, the expression of BC markers and downregulating TP53 expression. However, it is
such as ERCC1 and TP53 after T4 treatment is detected, noteworthy that the role of thyroid hormones in tumor
or in animal models, the correlation between marker biology remains complex and bidirectional. A recent
levels and tumor growth rate, recurrence rate, and other study demonstrated that T3 exhibits significant anti-
indicators is analyzed to provide an experimental basis tumor effects in a hepatocellular carcinoma model.
for prognosis assessment. Mutations in the TP53 gene The study found that T3 can activate the LKB1/AMPK/
and aberrant activation of the FGFR3 signaling pathway Raptor pathway by inducing thyroid hormone response
are frequently observed in BC cells. These molecular stimulatory protein, thereby inhibiting the abnormal
alterations are closely associated with changes in cell activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway, ultimately
proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion. Further research blocking the ENO -induced aerobic glycolysis process,
2
into the roles of TP53 and FGFR3 in these processes will and thus slowing down the metabolic progression and
help to elucidate their contribution to BC progression. growth of tumors. This study suggested that thyroid
45
Such studies will provide a theoretical foundation for the hormones may exhibit opposing biological effects
development of novel therapeutic targets and treatment depending on different tissue types, receptors, or
44
strategies. Second, retrospective or prospective clinical signaling pathway dependencies. This discrepancy may
studies are carried out to compare thyroid function be partially attributed to the distinct receptor selectivity
parameters (especially serum T4 and TSH levels) between and signaling mechanisms of T3 and T4. T3 primarily
BC patients and age-matched healthy individuals. Analyze mediates gene transcription regulation by binding to
whether the proportion of subclinical hyperthyroidism nuclear thyroid hormone receptors (TRα/TRβ), whereas
(low TSH, high normal T4) is higher among BC patients, T4 has been found to bind to the integrin αVβ3 receptor
or whether there is a correlation between T4 levels and in a non-genomic manner, rapidly activating signaling
BC staging/prognosis. If it is found that elevated thyroid pathways such as MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT, thereby
hormone levels or thyroid dysfunction in BC patients promoting cell proliferation and angiogenesis. 46,47
are associated with tumor severity, it would suggest that Therefore, even as thyroid hormones, their impact on
T4 may have clinical relevance in tumor development tumors may exhibit tissue specificity, dose dependency,
and progression. Through the above research directions, and receptor distribution dependency. In this study,
we hope to effectively address the limitations of current sustained T4 treatment in a mouse model led to elevated
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2025) 208 doi: 10.36922/EJMO025080037