Page 283 - EJMO-9-2
P. 283
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology QGJSF multi-target mechanisms in osteoporosis
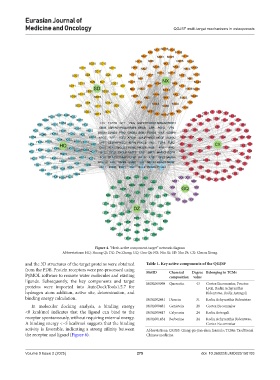
Figure 4. “Herb-active component-target” network diagram
Abbreviations: HQ: Huang Qi; DZ: Du Zhong; GQ: Gou Qi; NX: Niu Xi; SD: Shu Di; CX: Chuan Xiong.
and the 3D structures of the target proteins were obtained Table 1. Key active components of the QGJSF
from the PDB. Protein receptors were pre-processed using MolID Chemical Degree Belonging to TCMs
PyMOL software to remove water molecules and existing composition value
ligands. Subsequently, the key components and target MOL000098 Quercetin 43 Cortex Eucommiae, Fructus
proteins were imported into AutoDockTools1.5.7 for Lycii, Radix Achyranthis
hydrogen atom addition, active site, determination, and Bidentatae, Radix Astragali
binding energy calculation. MOL002441 Dioscin 31 Radix Achyranthis Bidentatae
In molecular docking analysis, a binding energy MOL000481 Genistein 28 Cortex Eucommiae
<0 kcal/mol indicates that the ligand can bind to the MOL000417 Calycosin 24 Radix Astragali
receptor spontaneously, without requiring external energy. MOL001454 Berberine 24 Radix Achyranthis Bidentatae,
A binding energy <−5 kcal/mol suggests that the binding Cortex Eucommiae
activity is favorable, indicating a strong affinity between Abbreviations: QGJSF: Qiang-gu-jian-shen formula; TCMs: Traditional
the receptor and ligand (Figure 6). Chinese medicine.
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2025) 275 doi: 10.36922/EJMO025150103