Page 34 - EJMO-9-2
P. 34
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology Gut microbiome effects on obesity
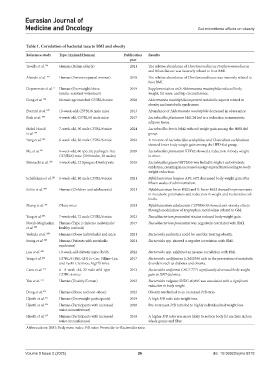
Table 1. Correlation of bacterial taxa to BMI and obesity
Reference study Type (Animal/Human) Publication Results
year
Tavella et al. 194 Human (Italian elderly) 2021 The relative abundance of Christensenellaceae Porphyromonadaceae
and Rikenellaceae was inversely related to host BMI.
Alemán et al. 195 Human (Postmenopausal women) 2018 The relative abundance of Christensenellaceae was inversely related to
host BMI.
Depommier et al. 11 Human (Overweight/obese 2019 Supplementation with Akkermansia muciniphila reduced body
insulin-resistant volunteers) weight, fat mass, and hip circumference.
Deng et al. 196 60 male age matched C57BL/6 mice 2020 Akkermansia muciniphila improved metabolic aspects related to
obesity and metabolic syndromes.
Everard et al. 197 10-week-old, C57BL/6 male mice 2013 Abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila decreased in obese mice.
Park et al. 198 4-week-old, C57BL/6J male mice 2017 Lactobacillus plantarum HAC01 led to a reduction in mesenteric
adipose tissue.
Mohd Hasali 7-week-old, 30 male C57BL/6 mice 2024 Lactobacillus brevis NJ42 reduced weight gain among the HFD-fed
et al. 199 group.
Yang et al. 200 6-week-old, 36 male C57BL/6 mice 2022 A mixture of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Clostridium cochlearium
showed lower body weight gain among the HFD-fed group.
Mu et al. 201 6-week-old, 60 specific pathogen-free 2020 Lactobacillus plantarum KFY02 showed a reduction in body weight
C57/BL6J mice (30 females, 30 males) in mice.
Shirouchi et al. 202 4-week-old, 12 Sprague–Dawley rats 2016 Lactobacillus gasseri SBT2055 was linked to higher carbohydrate
oxidation, resulting in increased energy expenditure leading to body
weight reduction.
Schellekens et al. 203 5-week-old, 40 male C57BL/6 mice 2021 Bifidobacterium longum APC1472 decreased body weight gain after
fifteen weeks of administration.
Solito et al. 204 Human (Children and adolescents) 2021 Bifidobacterium breve BR03 and B. breve B632 showed improvements
in metabolic parameters and reduction in weight and Escherichia coli
levels.
Zhang et al. 205 Obese mice 2024 Bifidobacterium adolescentis CCFM8630 showed anti-obesity effects
through modulation of tryptophan metabolism related to GM.
Yang et al. 206 7-week-old, 72 male C57BL/6 mice 2023 Faecalibacterium prausnitzii strains reduced body weight gain.
Navab-Moghadam Human (Type 2 diabetes individuals/ 2017 Faecalibacterium prausnitzii was negatively correlated with BMI.
et al. 207 healthy controls)
Yoshida et al. 208 Human (Obese individuals) and mice 2021 Bacteroides probiotics could be used for treating obesity.
Seong et al. 209 Human (Patients with metabolic 2021 Bacteroides spp. showed a negative correlation with BMI.
syndrome)
Luo et al. 210 10-week-old diabetic mice db/db. 2022 Bacteroides spp. exhibited an inverse correlation with BMI.
Yang et al. 211 C57BL/6 (B6), CD11c-Cre, Villine-Cre, 2017 Bacteroides acidifaciens JCM10556 aids in the prevention of metabolic
and LysM-Cre mice; Atg7f/f mice disorders such as diabetes and obesity.
Cano et al. 212 6 – 8-week-old, 32 male wild-type 2012 Bacteroides uniformis CECT 7771 significantly decreased body weight
C57BL-6 mice gain in HFD‑fed mice.
You et al. 213 Human (Healthy Korean) 2023 Bacteroides vulgatus SNUG 40,005 was associated with a significant
reduction in body weight.
Dong et al. 214 Human (Obese and non-obese) 2022 Obesity was linked to an increased P/B ratio.
Hjorth et al. 215 Human (Overweight participants) 2019 A high P/B ratio aids weight loss.
Hjorth et al. 216 Human (Participants with increased 2020 Pre-treatment P/B ratio led to highly individualized weight loss.
waist circumference)
Hjorth et al. 217 Human (Participants with increased 2018 A higher P/B ratio was more likely to reduce body fat on diets rich in
waist circumference) whole grains and fiber.
Abbreviations: BMI; Body mass index; P/B ratio: Prevotella-to-Bacteroides ratio.
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2025) 26 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.8318