Page 100 - EJMO-9-3
P. 100
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology Novel senescence-based melanoma risk model
A B
C
D E
F
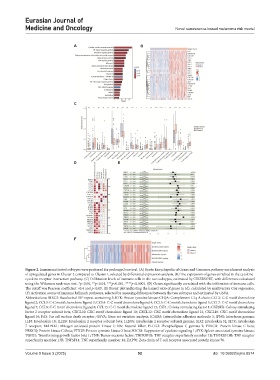
Figure 2. Immunoactivated subtypes were preferred for prolonged survival. (A) Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway enrichment analysis
of upregulated genes in Cluster 2 compared to Cluster 1, selected by differential expression analysis. (B) The expression of genes enriched in the cytokine-
cytokine receptor interaction pathway. (C) Infiltration levels of immune cells in the two subtypes, estimated by CIBERSORT, with differences calculated
using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. (D) Genes significantly correlated with the infiltration of immune cells.
The cutoff was Pearson coefficient >0.4 and p<0.05. (E) Forest plot indicating the hazard ratio of genes in (d), calculated by multivariate Cox regression.
(F) Activation scores of immune hallmark pathways, selected by assessing differences between the two subtypes and estimated by GSVA.
Abbreviations: BIRC3: Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 3; BTK: Bruton tyrosine kinase; C1QA: Complement C1q A chain; CCL2: C-C motif chemokine
ligand 2; CCL3: C-C motif chemokine ligand 3; CCL4: C-C motif chemokine ligand 4; CCL5: C-C motif chemokine ligand 5; CCL7: C-C motif chemokine
ligand 7; CCL8: C-C motif chemokine ligand 8; CCL13: C-C motif chemokine ligand 13; CSF1: Colony stimulating factor 1; CSF2RB: Colony stimulating
factor 2 receptor subunit beta; CXCL10: CXC motif chemokine ligand 10; CXCL12: CXC motif chemokine ligand 12; CXCL16: CXC motif chemokine
ligand 16; FAS: Fas cell surface death receptor; GSVA: Gene set variation analysis; ICAM3: Intercellular adhesion molecule 3; IFNG: Interferon gamma;
IL18: Interleukin 18; IL2RB: Interleukin 2 receptor subunit beta; IL2RG: Interleukin 2 receptor subunit gamma; IL32: Interleukin 32; IL7R: Interleukin
7 receptor; MAP4K1: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1; NK: Natural killer; PLCG2: Phospholipase C gamma 2; PRKCB: Protein kinase C beta;
PRKCQ: Protein kinase C theta; PTK2B: Protein tyrosine kinase 2 beta; SOCS1: Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1; SYK: Spleen associated tyrosine kinase;
TGFB1: Transforming growth factor beta 1; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TNFRSF1B: TNF receptor superfamily member 1B; TNFRSF13B: TNF receptor
superfamily member 13B; TNFSF14: TNF superfamily member 14; ZAP70: Zeta chain of T cell receptor associated protein kinase 70.
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2025) 92 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.8574