Page 102 - EJMO-9-3
P. 102
Eurasian Journal of
Medicine and Oncology Novel senescence-based melanoma risk model
A B
C D
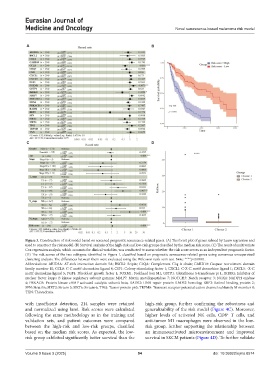
Figure 3. Construction of risk model based on screened prognostic senescence-related genes. (A) The forest plot of genes refined by Lasso regression and
used to construct the risk model. (B) Survival analysis of the high-risk and low-risk groups classified by the median risk score. (C) The result of multivariate
Cox regression analysis, which accounts for clinical variables, was conducted to assess whether the risk score serves as an independent prognostic factor.
(D) The risk scores of the two subtypes identified in Figure 1, classified based on prognostic senescence-related genes using consensus unsupervised
clustering analysis. The differences between them were evaluated using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Note: ****p<0.0001.
Abbreviations: ARID5A: AT-rich interaction domain 5A; BSCL2: Seipin; C1QA: Complement C1q A chain; CARD10: Caspase recruitment domain
family member 10; CCL8: C-C motif chemokine ligand 8; CSF1: Colony stimulating factor 1; CXCL1: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 1; CXCL5: -X-C
motif chemokine ligand 5; FGF1: Fibroblast growth factor 1; FOXM1: Forkhead box M1; GSTP1: Glutathione S-transferase pi 1; IKBKG: Inhibitor of
nuclear factor kappa B kinase regulatory subunit gamma; MMP7: Matrix metallopeptidase 7; NOTCH3: Notch receptor 3; NOX4: NADPH oxidase
4; PRKACB: Protein kinase cAMP-activated catalytic subunit beta; RAD52: DNA repair protein RAD52 homolog; RBP2: Retinol binding protein 2;
SFN: Stratifin; SIRT3: Sirtuin 3; SIRT6: Sirtuin 6; TP63: Tumor protein p63; TRPM8: Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 8;
TXN: Thioredoxin.
with insufficient detection, 214 samples were retained high-risk group, further confirming the robustness and
and normalized using lumi. Risk scores were calculated generalizability of the risk model (Figure 4C). Moreover,
following the same methodology as in the training and higher levels of activated NK cells, CD8 T cells, and
+
validation sets, and patient outcomes were compared anti-tumor M1 macrophages were observed in the low-
between the high-risk and low-risk groups, classified risk group, further supporting the relationship between
based on the median risk scores. As expected, the low- an immunoactivated microenvironment and improved
risk group exhibited significantly better survival than the survival in SKCM patients (Figure 4D). To further validate
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2025) 94 doi: 10.36922/ejmo.8574