Page 27 - GHES-2-1
P. 27
Global Health Econ Sustain Global South: Healthier lives with UVC
that emit nearly monochromatic irradiation at 254 nm is consumed or used for sanitation and hygiene purposes
or polychromatic irradiation (200+ nm), respectively, (Li et al., 2019).
absorbed by nucleic acids in microorganisms. Several action spectra studies have proven a direct
Unlike conventional UVC lamps, UVC LEDs are correlation between the spectral sensitivity of DNA
compact, have lower energy demands, and operate on and RNA and the absorbance spectrum of the tested
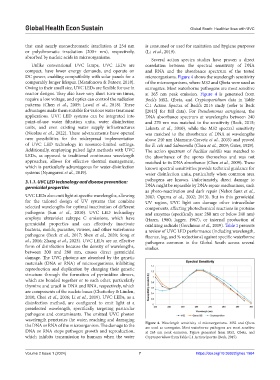
DC power, enabling compatibility with solar panels for a microorganisms. Figure 4 shows the wavelength sensitivity
comparably longer lifespan (Matafonova & Batoev, 2018). of the microorganisms, where MS2 and Qbeta were used as
Owing to their small size, UVC LEDs are flexible for use in surrogates. Most waterborne pathogens are most sensitive
reactor designs. They also have very short turn-on times, at 265 nm peak emission. Figure 4 is generated from
require a low voltage, and optics can control the radiation Beck’s MS2, Qbeta, and Cryptosporidium data in Table
patterns (Chen et al., 2009; Lawal et al., 2018). These C.1 Action Spectra of Beck’s 2015 study (refer to Beck
advantages make them suitable for various water treatment [2015] for full data). For Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the
applications. UVC LED systems can be integrated into DNA absorbance spectrum at wavelengths between 240
point-of-use water filtration units, water disinfection and 270 nm was matched to the sensitivity (Beck, 2015;
units, and even existing water supply infrastructures Lakretz et al., 2010), while the MS2 spectral sensitivity
(Nicolau et al., 2022). These advancements have opened was matched to the absorbance of DNA at wavelengths
new possibilities for the widespread implementation above 240 nm (Mamane-Gravetz et al., 2005) and proved
of UVC LED technology in resource-limited settings. for E. coli and Salmonella (Chen et al., 2009; Gates, 1929).
Additionally, employing pulsed light methods with UVC The action spectrum of Bacillus subtilis was matched to
LEDs, as opposed to traditional continuous wavelength the absorbance of the spores themselves and was not
approaches, allows for effective thermal management, matched to its DNA absorbance (Chen et al., 2009). These
which is particularly advantageous for water-disinfection known spectral sensitivities provide technical guidance for
systems (Nyangaresi et al., 2019). water disinfection units, particularly when common area
3.1.1. UVC LED technology and disease prevention: pathogens are known. Unfortunately, direct damage to
germicidal properties DNA might be reparable by DNA-repair mechanisms, such
as photo-reactivation and dark repair (Nebot Sanz et al.,
UVC LEDs also emit light at specific wavelengths, allowing 2007; Oguma et al., 2002; 2013). But in this germicidal
for the tailored design of UV systems that combine UV region, UVC light can damage other intracellular
selected wavelengths for optimal inactivation of different components, affecting photochemical reactions in proteins
pathogens (Sun et al., 2010). UVC LED technology and enzymes (specifically near 280 nm or below 240 nm)
employs ultraviolet subtype C emissions, which have (Harm, 1980; Jagger, 1967), or internal production of
germicidal properties and can effectively inactivate oxidizing radicals (Gerchman et al., 2019). Table 1 presents
bacteria, molds, parasites, viruses, and other waterborne a review of UVC LED performance (including wavelength,
pathogens (Beck et al., 2017; Shen et al., 2020; Song et fluence, log, and % reductions) against specific waterborne
al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2023). UVC LEDs are an effective pathogens common in the Global South across several
form of disinfection because the density of wavelengths, studies.
between 200 and 280 nm, causes direct germicidal
damage. The UVC photons are absorbed by the genetic
materials (DNA or RNA) of microorganisms, inhibiting
reproduction and duplication by changing their genetic
structure through the formation of pyrimidine dimers,
which are bonded together or to each other, particularly
thymine and uracil in DNA and RNA, respectively, which
are components of the nucleic bases (Chatterley & Linden,
2010; Choi et al., 2006; Li et al., 2019). UVC LEDs, as a
disinfection method, are configured to emit light at a
preselected wavelength, specifically targeting particular
pathogens and contaminants. The emitted UVC photon
wavelength penetrates the water, reaching and damaging
the DNA or RNA of the microorganism. The damage to the Figure 4. Wavelength sensitivity of microorganisms. MS2 and Qbeta
are used as surrogates. Most waterborne pathogens are most sensitive
DNA or RNA stops pathogen growth and reproduction, at 265 nm peak emission. Figure generated from MS2, Qbeta, and
which inhibits transmission to humans when the water Cryptosporidium from Table C.1 Action Spectra (Beck, 2015).
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2024) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.1984