Page 72 - GHES-2-1
P. 72
Global Health Econ Sustain Quantum Data Lake for epidemic analysis
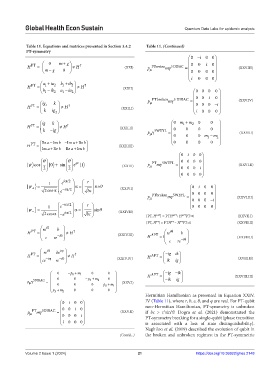
Table 11. Equations and matrices presented in Section 3.4.2 Table 11. (Continued)
PT‑symmetry
0 − i 0 0
+
†
H PT = 0 mg ≠ H (XXI) p PTbroken mγ 5 DIRAC = 0 0 i 0 (XXV.III)
− 0 mg µ 0 0 00
i 0 0 0
a + ia b + ib
H PT = 1 2 1 2 ≠ H † (XXII)
b − ib 2 a − ia 2 000 0
1
1
00 i 0
ig k p µ PTbroken mγ 5 DIRAC = 000 − i (XXV.IV)
H PT = k 1 ig 2 ≠ H † (XXII.I) i 00 0
ig k 0 m + m 2 0 0
1
†
H PT = k − ig ≠ H (XXII.II) p γ 5WEYL = 0 0 0 0 0 m − 0 m (XXVI.I)
0
µ
b
Im
Re
a +
H PT = Re a − Im b − Re a + Im b (XXII.III) 0 0 0 1 0 2
b
a +
Re
Im
0 i 0 0
θ θ 0000
|ψ cos |0 + sin e ϕi |1 (XXIII) p µ PT mγ 5WEYL = 000 i (XXVI.II)
2
2
0000
2
e
1 i α / r
|ψ + = α = sin θ 0 i 0 0
2 cosα e − αi /2 bc (XXIV.I) 000 0
p µ PTbroken mγ 5WEYL = 000 − i (XXVI.III)
2
1 e − αi / r 000 0
|ψ − = α = sin θ
2
2 cosα −e α i / bc (XXIV.II) [PT, H APT ] = PTH APT +H APT PT=0 (XXVII.I)
PT
[PT, H ] = PTH – H PT=0 (XXVII.II)
PT
PT
re iθ b
H PT = ≠ H † APT re iθ b
c re i −θ (XXIV.III) H = i c re − θ (XXVIII.I)
i
re iθ be iϕ − ig ik
H PT = ≠ H † H APT =
ce i −ϕ e r i −θ (XXIV.IV) ik ig (XVIII.II)
0 − p + m 1 0 0 APT − ig − ik
0
0 0 − p + m 0 H = − ik (XXVIII.III)
p γ 5DIRAC = 0 0 3 0 2 p + m (XXV.I) ig
µ
0 1
p +
3 m 2 0 0 0
Hermitian Hamiltonian as presented in Equation XXIV.
0 i 0 0 IV (Table 11), where r, b, c, θ, and φ are real. For PT-qubit
00 i 0 non-Hermitian Hamiltonian, PT-symmetry is unbroken
2
p µ PT mγ 5DIRAC = 000 i (XXV.II) if bc > r sin θ. Dogra et al. (2021) demonstrated the
2
PT-symmetry breaking for a single-qubit (phase transition
i 000 is associated with a loss of state distinguishability).
Naghiloo et al. (2019) described the evolution of qubit in
(Cont’d...) the broken and unbroken regimes; in the PT-symmetric
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2024) 21 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.2148