Page 48 - GPD-2-1
P. 48
Gene & Protein in Disease NQO2 and dopamine toxicity versus detoxification
the synthetic N-benzyl-dihydronicotinamide (BNAH) diseases, at least in some occurrences [26,27] . The definition of
or the natural ones: N-methyl-dihydronicotinamide dopaminergic neurons corresponds to neurons expressing
(NMH) and N-ribosyl-dihydronicotinamide (NRH). The the tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), an enzyme responsible for
concentration of the latter remains mostly elusive in resting the biosynthesis of dopamine from tyrosine . O-quinone
[28]
tissues [14-16] . This very fact has led to a key controversy on toxicity has been attributed to the auto-oxidation capacity of its
whether NQO2 is an enzyme with catalytic activity or a oxidized form , although alternative or parallel hypotheses
[29]
pseudo-enzyme without catalytic activity , although it had been explored. The link between dopaminequinone and
[17]
remains clear that the same enzyme, NQO2, is present Parkinson’s disease has been reviewed [30-32] .
in the genome for several millions of years with the same
unique co-substrate recognition as it has been cloned from Hydroxylated molecules are eliminated from the body by
Anas platyrhynchos and Alligator mississippiensis . The key enzymatic conjugations with polar moieties, such as sulfates
[17]
questions, which remain unanswered, include: (i) What is or glucuronic acids. These molecules can be endobiotes
its natural co-substrate? Is it NRH? (ii) Where does it come (bilirubin, steroids, biliary acids, etc.) or xenobiotes
[33,34]
from? Obviously, in tubo or in cellulo, the enzyme works (terpenoids, pollutants, and polyaromatic compounds) .
catalytically and functionally with these co-substrates [11,18,19] . If not already hydroxylated, they are substrates of the large
[35]
NQO2 reduces o- and p-quinones when the co-substrate cytochrome P450 family of enzymes . These enzymes,
is provided to the pure enzyme [8,13] . NQO2 might have a cytochromes P450 and UDP-glucuronosyltransferases
preferred specificity towards o-quinones . This activity (UGT), are mostly expressed in key organs, that is, liver and
[20]
also has a “functional” by-product: because the o-quinols are kidneys, but also exist in numerous other organs, such as
particularly unstable, in aerobic conditions, they reversed to skin and brain [36,37] . UGT, in particular, is clearly active in
their more stable quinone version, while producing ROS [8,20] . the brain [38-43] . Incidentally, it has been demonstrated that
Therefore, quinone reductases, by producing diols, indirectly morphine glucuronide is more active than its aglycone-
produce ROS species [5,6] in a futile cycle. morphine itself [44,45] . Dopamine glucuronides were identified
in mammalian organs and blood [46-51] and found in brain [52-54] .
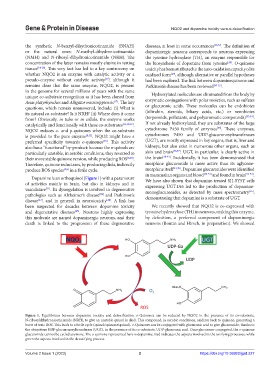
Dopamine is an orthoquinol (Figure 1) with a paramount We have also shown that dopamine-treated SH-SY5Y cells
of activities mainly in brain, but also in kidneys and in expressing UGT1A6 led to the production of dopamine-
vasculature . Its dysregulation is involved in degenerative monoglucuronides, as detected by mass spectrometry ,
[21]
[55]
pathologies such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s demonstrating that dopamine is a substrate of UGT.
[22]
disease , and in general, in neurotoxicity . A link has
[24]
[23]
been suspected for decades between dopamine toxicity We recently showed that NQO2 is co-expressed with
and degenerative diseases . Neurons highly expressing tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) in neurons, making this enzyme,
[25]
this molecule are named dopaminergic neurons, and their by definition, a preferred component of dopaminergic
death is linked to the progression of these degenerative neurons (Boutin and Hirsch, in preparation). We showed
Figure 1. Equilibrium between dopamine toxicity and detoxification. o-Quinones can be reduced by NQO2 in the presence of its co-substrate,
N-ribosyldihydronicotinamide (NRH), to give an unstable quinol (a diol). This compound, in aerobic conditions, oxidizes back to quinone, generating a
burst of toxic ROS. This leads to a futile cycle (quinol/quinone/quinol). o-Quinones can be conjugated with glucuronic acid to give glucuronide, thanks to
the ubiquitous UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT), in the presence of its co-substrate, UDP-glucuronic acid. Once glucurono-conjugated, the o-quinone
glucuronide cannot be cycled anymore. The o-quinone represented here is dopamine. Red indicates the aspects involved in the toxifying processes, while
green the aspects involved in the detoxifying process.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 2 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.227