Page 50 - GPD-2-1
P. 50
Gene & Protein in Disease NQO2 and dopamine toxicity versus detoxification
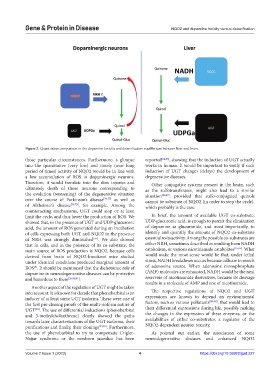
Figure 2. Quantitative comparison in the dopamine toxicity and detoxification equilibrium between liver and brain.
those particular circumstances. Furthermore, a glimpse reported [84,85] , showing that the induction of UGT actually
into the quantitative (very low) and timely (over long works in human. It would be important to verify if such
period of times) activity of NQO2 would be in line with induction of UGT changes (delays) the development of
a low accumulation of ROS in dopaminergic neurons. degenerative diseases.
Therefore, it would translate into the slow injuries and Other conjugative systems present in the brain, such
ultimately death of those neurons corresponding to as the sulfotransferases, might also lead to a similar
the evolution (worsening) of the degenerative situation situation [86,87] , provided that sulfo-conjugated quinols
over the course of Parkinson’s disease [76,77] as well as cannot be substrate of NQO2 (in order to stop the cycle),
of Alzheimer’s disease [78,79] , for example. Among the which probably is the case.
counteracting mechanisms, UGT could stop or at least
limit the cycle, and thus lower the production of ROS. We In brief, the amount of available UGT co-substrate,
showed that, in the presence of UGT and UDP-glucuronic UDP-glucuronic acid, is enough to permit the elimination
acid, the amount of ROS generated during an incubation of dopamine as glucuronide, and most importantly, to
of cells expressing both UGT and NQO2 in the presence identify and quantify the amount of NQO2 co-substrate
of NRH was strongly diminished . We also showed essential to its activity. Among the possible co-substrates are
[55]
that in cells, and in the presence of its co-substrate, the either NRH, sometimes described as resulting from NADH
main source of ROS production is NQO2, because cells catabolism, or various nicotinamide catabolites [15,16] . What
derived from brain of NQO2-knockout mice studied would make the most sense would be that, under lethal
under identical conditions produced marginal amount of stress, NADH breakdown occurs because cells are in search
ROS . It should be mentioned that the dichotomic role of of adenosine source. When adenosine monophosphate
[9]
dopamine in neurodegenerative diseases can be protective (AMP) molecules are exhausted, NADH would be the next
and hazardous to them [26,80,81] . reservoir of nicotinamide derivatives, because its cleavage
results in a molecule of AMP and one of nicotinamide.
Another aspect of the regulation of UGT might be taken
into account. It is known for decade that phenobarbital is an The respective regulations of NQO2 and UGT
inducer of at least some UGT isoforms. These were one of expressions are known to depend on environmental
[88-90]
the first pre-cloning proofs of the multi-isoform nature of factors, such as various pollutants , that would lead to
UGT . The use of differential inductions (phenobarbital their differential expressions during life, possibly making
[82]
and 3-methylcholanthrene) clearly showed the paths the changes in the expression of these enzymes, or the
towards later characterizations of the UGT isoforms, their availabilities of either co-substrates, a regulator of the
purifications and finally, their clonings [33,83] . Furthermore, NQO2-dependent neuron toxicity.
the use of phenobarbital to try to compensate Crigler- As pointed out earlier, the association of some
Najjar syndrome or the newborn jaundice has been neurodegenerative diseases and enhanced NQO2
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.227