Page 77 - GPD-2-4
P. 77
Gene & Protein in Disease Carpenter bee a substrate for green synthesis
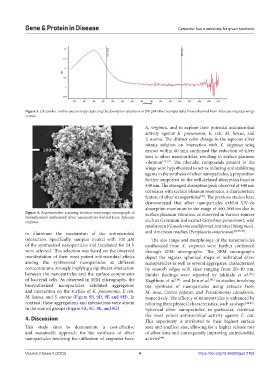
Figure 3. Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy depicting the absorption spectrum of 290 µM silver nanoparticles biosynthesized from Xylocopa virginica wings
extract.
X. virginica, and to explore their potential antimicrobial
activity against K. pneumonia, E. coli, M. luteus, and
S. aureus. The distinct color change in the aqueous silver
nitrate solution on interaction with X. virginica wing
extract within 60 min confirmed the reduction of silver
ions to silver nanoparticles, resulting in surface plasmon
vibration [35-37] . The phenolic compounds present in the
wings were hypothesized to act as reducing and stabilizing
agents in the synthesis of silver nanoparticles, a proposition
further supported by the well-defined absorption band at
440 nm. The strongest absorption peak observed at 440 nm
correlates with surface plasmon resonance, a characteristic
feature of silver nanoparticles . The previous studies have
[38]
demonstrated that silver nanoparticles exhibit UV-vis
absorption maximum in the range of 400–500 nm due to
Figure 4. Representative scanning electron microscopy micrograph of surface plasmon vibration, as observed in various sources
biosynthesized synthesized silver nanoparticles derived from Xylocopa
virginica. such as Geranium leaf extract (Strychnos potatorum), wild
mushroom (Ganoderma sessiliforme), termites (Mang mao),
to illuminate the mechanism of the antimicrobial and American roaches (Periplaneta americana) [32,38-40] .
interaction. Specifically, samples treated with 100 µM The size range and morphology of the nanoparticles
of the synthesized nanoparticles and incubated for 24 h synthesized from X. virginica were further confirmed
were selected. This selection was based on the observed through SEM micrographs. The SEM micrographs
manifestation of their most potent antimicrobial effects depict the regular, spherical shape of individual silver
among the synthesized nanoparticles at different nanoparticles as well as several aggregates, characterized
concentrations, strongly implying a significant interaction by smooth edges with sizes ranging from 20–40 nm.
between the nanoparticles and the surface components Similar findings were reported by Jakinala et al. ,
[32]
of bacterial cells. As observed in SEM micrographs, the Kagithoju et al. , and Jain et al. in studies involving
[38]
[41]
biosynthesized nanoparticles exhibited aggregation the synthesis of nanoparticles using extracts from
and interaction on the surface of K. pneumonia, E coli, M. mao, Carica papaya, and Pseudomonas canadensis,
M. luteus, and S. aureus (Figure 9B, 9D, 9F, and 9H). In respectively. The efficacy of nanoparticles is enhanced by
contrast, these aggregations and interactions were absent tailoring their physical characteristics, such as shape [42,43] .
in the control groups (Figure 9A, 9C, 9E, and 9G). Spherical silver nanoparticles, in particular, exhibited
the most potent antimicrobial activity against E. coli.
4. Discussion This superiority is attributed to their highest surface
This study aims to demonstrate a cost-effective area and smallest size, allowing for a higher release rate
and sustainable approach for the synthesis of silver of silver ions and consequently improving antimicrobial
nanoparticles involving the utilization of carpenter bees, activity .
[44]
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.2155