Page 118 - GPD-3-2
P. 118
Gene & Protein in Disease The effect of myostatin on muscle-related miRNAs
A
B C
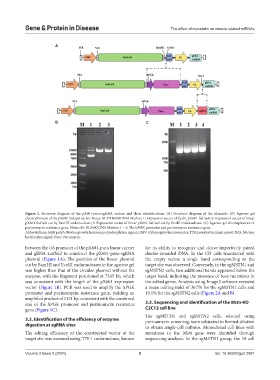
Figure 1. Structure diagram of the pX601-puro-sgRNA vectors and their identifications. (A) Structure diagram of the plasmids. (B) Agarose gel
electrophoresis of the pX601-SaCas9 vector. Notes: M: DL10000 DNA Marker; 1: Expression vector of Cyclic pX601-SaCas9; 2: Expression vector of linear
pX601-SaCas9 cut by BamHI endonuclease; 3: Expression vector of linear pX601-SaCas9 cut by EcoRI endonuclease. (C) Agarose gel electrophoresis of
purinomycin resistance gene. Notes: M: DL2000 DNA Marker; 1 – 4: The hPGK promoter and purinomycin resistance gene.
Abbreviations: bGH polyA: Bovine growth hormone polyadenylation signal; CMV: Cytomegalovirus promoter; ITR: Inverted terminal repeat; NLS: Nuclear
localization signal; Puro: Puromycin.
between the U6 promoter of the pX601-puro linear carrier for its ability to recognize and cleave imperfectly paired
and gRNA scaffold to construct the pX601-puro-sgRNA double-stranded DNA. In the CN cells transfected with
plasmid (Figure 1A). The position of the linear plasmid the empty vector, a single band corresponding to the
cut by BamHI and EcoRI endonucleases in the agarose gel target site was observed. Conversely, in the sgMSTN1 and
was higher than that of the circular plasmid without the sgMSTN2 cells, two additional bands appeared below the
enzyme, with the fragment positioned at 7345 bp, which target band, indicating the presence of base mutations in
was consistent with the length of the pX601 expression the edited genes. Analysis using Image J software revealed
vector (Figure 1B). PCR was used to amplify the hPGK a mean editing indel of 30.7% for the sgMSTN1 cells and
promoter and purinomycin resistance gene, yielding an 19.1% for the sgMSTN2 cells (Figure 2A and B).
amplified product of 1121 bp, consistent with the combined
size of the hPGK promoter and purinomycin resistance 3.3. Sequencing and identification of the Mstn-KO
gene (Figure 1C). C2C12 cell line
The sgMSTN1 and sgMSTN2 cells, selected using
3.2. Identification of the efficiency of enzyme purinamycin screening, were subjected to limited dilution
digestion at sgRNA sites to obtain single-cell cultures. Monoclonal cell lines with
The editing efficiency of the constructed vector at the mutations in the Mstn gene were identified through
target site was assessed using T7E I endonuclease, known sequencing analysis. In the sgMSTN1 group, the 1# cell
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 5 doi: 10.36922/gpd.2991