Page 121 - GPD-3-2
P. 121
Gene & Protein in Disease The effect of myostatin on muscle-related miRNAs
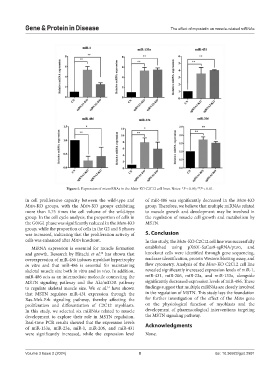
Figure 5. Expression of microRNAs in the Mstn-KO C2C12 cell lines. Notes: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.
in cell proliferative capacity between the wild-type and of miR-486 was significantly decreased in the Mstn-KO
Mstn-KO groups, with the Mstn-KO groups exhibiting group. Therefore, we believe that multiple miRNAs related
more than 1.75 times the cell volume of the wild-type to muscle growth and development may be involved in
group. In the cell cycle analysis, the proportion of cells in the regulation of muscle cell growth and metabolism by
the G0/G1 phase was significantly reduced in the Mstn-KO MSTN.
group, while the proportion of cells in the G2 and S phases
was increased, indicating that the proliferation activity of 5. Conclusion
cells was enhanced after Mstn knockout. In this study, the Mstn-KO C2C12 cell line was successfully
MiRNA expression is essential for muscle formation established using pX601-SaCas9-sgRNA/puro, and
and growth. Research by Hitachi et al. has shown that knockout cells were identified through gene sequencing,
30
overexpression of miR-486 induces myoblast hypertrophy nuclease identification, protein Western blotting assay, and
in vitro and that miR-486 is essential for maintaining flow cytometry. Analysis of the Mstn-KO C2C12 cell line
skeletal muscle size both in vitro and in vivo. In addition, revealed significantly increased expression levels of miR-1,
miR-486 acts as an intermediate molecule connecting the miR-431, miR-206, miR-23a, and miR-133a, alongside
MSTN signaling pathway and the Akt/mTOR pathway significantly decreased expression levels of miR-486. These
to regulate skeletal muscle size. Wu et al. have shown findings suggest that multiple miRNAs are closely involved
31
that MSTN regulates miR-431 expression through the in the regulation of MSTN. This study lays the foundation
Ras-Mek-Erk signaling pathway, thereby affecting the for further investigation of the effect of the Mstn gene
proliferation and differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts. on the physiological function of myoblasts and the
In this study, we selected six miRNAs related to muscle development of pharmacological interventions targeting
development to explore their role in MSTN regulation. the MSTN signaling pathway.
Real-time PCR results showed that the expression levels Acknowledgments
of miR-133a, miR-23a, miR-1, miR-206, and miR-431
were significantly increased, while the expression level None.
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 8 doi: 10.36922/gpd.2991