Page 129 - GPD-3-2
P. 129
Gene & Protein in Disease Bioinformatics to identify gene signatures of CF
A
B C
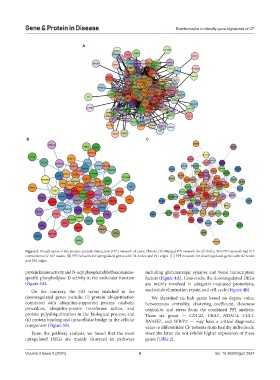
Figure 5. Visualization of the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network of cystic fibrosis. (A) Merged PPI network for all DEGs. This PPI network had 515
connections for 167 nodes. (B) PPI network for upregulated genes with 74 nodes and 191 edges. (C) PPI network for downregulated genes with 82 nodes
and 282 edges.
protein kinase activity and N-acyl phosphatidylethanolamine- including glutamatergic synapse and basal transcription
specific phospholipase D activity in the molecular function factors (Figure 4A). Conversely, the downregulated DEGs
(Figure 3A). are mainly involved in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis,
On the contrary, the GO terms enriched in the nucleotide elimination repair, and cell cycle (Figure 4B).
downregulated genes include: (i) protein ubiquitination We identified six hub genes based on degree value,
connected with ubiquitin-supported protein catabolic betweenness centrality, clustering coefficient, closeness
procedure, ubiquitin-protein transferase action, and centrality, and stress from the combined PPI analysis.
protein polyubiquitination in the biological process; and These six genes — CDC42, UBA2, HDAC4, CUL1,
(ii) protein binding and intracellular bridge in the cellular RNASEL, and WWP2 — may have a critical diagnostic
component (Figure 3B). value to differentiate CF patients from healthy individuals,
From the pathway analysis, we found that the most since the latter do not exhibit higher expression of these
upregulated DEGs are mainly clustered in pathways genes (Table 2).
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 6 doi: 10.36922/gpd.2937