Page 152 - GPD-4-1
P. 152
Gene & Protein in Disease FXR1 modulates gene expression in cancer
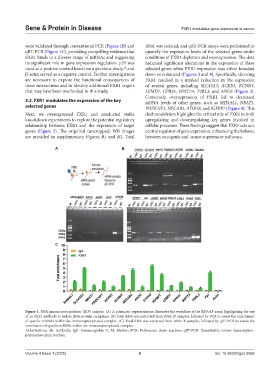
were validated through conventional PCR (Figure 1B) and RNA was isolated, and qRT-PCR assays were performed to
qRT-PCR (Figure 1C), providing compelling evidence that quantify the expression levels of the selected genes under
FXR1 binds to a diverse range of mRNAs and suggesting conditions of FXR1 depletion and overexpression. The data
its significant role in gene expression regulation. p21 was indicated significant alterations in the expression of these
used as a positive control based on a previous study, and selected genes when FXR1 expression was either knocked
12
β-actin served as a negative control. Further investigations down or enhanced (Figures 3 and 4). Specifically, silencing
are necessary to explore the functional consequences of FXR1 resulted in a marked reduction in the expression
these interactions and to identify additional FXR1 targets of several genes, including SLC43A3, ACKR3, KCNN3,
that may have been overlooked in this study. LEMD1, GPR35, WNT7A, F2RL3, and ANO5 (Figure 3).
Conversely, overexpression of FXR1 led to decreased
3.2. FXR1 modulates the expression of the key mRNA levels of other genes, such as SHISAL1, NBAT1,
selected genes PDZK1IP1, NECAB2, ATOH8, and IGFBP7 (Figure 4). This
Next, we overexpressed FXR1 and conducted stable dual modulation highlights the critical role of FXR1 in both
knockdown experiments to explore the potential regulatory upregulating and downregulating key genes involved in
relationship between FXR1 and the expression of target cellular processes. These findings suggest that FXR1 acts as a
genes (Figure 2). The origninal (uncropped) WB images central regulator of gene expression, influencing the balance
are provided in supplementary Figures R1 and R2. Total between oncogenic and tumor-suppressive pathways.
A B
C
Figure 1. RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) analysis. (A) A schematic representation illustrates the workflow of the RNA-IP assay, highlighting the use
of an FXR1 antibody to isolate RNA-protein complexes. (B) Total RNA was extracted from RNA-IP samples, followed by PCR to assess the enrichment
of specific mRNAs within the immunoprecipitated complex. (C) Total RNA was extracted from RNA-IP samples, followed by qRT-PCR to assess the
enrichment of specific mRNAs within the immunoprecipitated complex.
Abbreviations: Ab: Antibody; IgG: Immunoglobin G; M: Marker; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; qRT-PCR: Quantitative reverse transcription-
polymerase chain reaction.
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/gpd.5068