Page 153 - GPD-4-1
P. 153
Gene & Protein in Disease FXR1 modulates gene expression in cancer
A these mRNAs may indicate specificity in FXR1’s interaction
with certain mRNA subsets and highlight the importance
of specific structural or sequence conditions in identifying
binding motifs. This computational mapping provides a
foundational understanding of FXR1’s mRNA interactions
and underscores the need for further experimental
validation to gain insights into the role of FXR1 in post-
B
transcriptional regulation across various mRNA targets.
3.4. Correlation analysis of FXR1 with selected genes
Using the GEPIA database, we conducted a
comprehensive pairwise gene correlation analysis
utilizing expression data from both the TCGA and
GTEx datasets. This analysis aimed to explore the
relationship between FXR1 and a curated list of selected
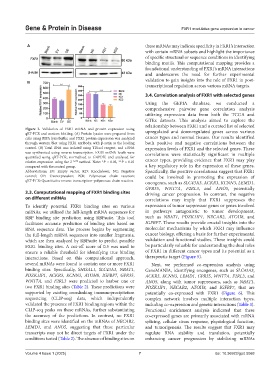
Figure 2. Validation of FXR1 mRNA and protein expression using upregulated and downregulated genes across various
qRT-PCR and western blotting. (A) Protein lysates were prepared from
cells using RIPA lysis buffer, and FXR1 protein expression was analyzed cancer types and normal tissues. Our results identified
through western blot using FXR1 antibody, with β-actin as the loading both positive and negative correlations between the
control. (B) Total RNA was isolated using TRIzol reagent, and cDNA expression levels of FXR1 and the selected genes. These
was synthesized using reverse transcription. FXR1 mRNA levels were correlations were statistically significant in multiple
quantified using qRT-PCR, normalized to GAPDH, and analyzed for cancer types, providing evidence that FXR1 may play
relative expression using the 2 −ΔΔCt method. Note: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01
compared with the control group. a key regulatory role in the expression of these genes.
Abbreviations: EV: Empty vector, KD: Knockdown; NC: Negative Specifically, the positive correlations suggest that FXR1
control; OE: Overexpression; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; could be involved in promoting the expression of
qRT-PCR: Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.
oncogenes, such as SLC43A3, ACKR3, KCNN3, LEMD1,
GPR35, WNT7A, F2RL3, and ANO5, potentially
3.3. Computational mapping of FXR1 binding sites driving cancer progression. In contrast, the negative
on different mRNAs correlations may imply that FXR1 suppresses the
To identify potential FXR1 binding sites on various expression of tumor suppressor genes or genes involved
mRNAs, we utilized the full-length mRNA sequences for in pathways antagonistic to tumor development,
RBP binding site prediction using RBPsuite. This tool such as NBAT1, PDZK1IP1, NECAB2, ATOH8, and
facilitates accurate prediction of binding sites based on IGFBP7. These results provide crucial insights into the
RNA sequence data. The process begins by segmenting molecular mechanisms by which FXR1 may influence
the full-length mRNA sequences into smaller fragments, cancer biology, offering a basis for further experimental
which are then analyzed by RBPsuite to predict possible validation and functional studies. These insights could
FXR1 binding sites. A cut-off score of 0.5 was used to be particularly valuable for understanding the dual roles
ensure a reliable threshold for identifying true binding of FXR1 in different cancer types and its potential as a
interactions. Based on this computational approach, therapeutic target (Figure 5).
several mRNAs were found to contain one or more FXR1 Next, we performed co-expression analysis using
binding sites. Specifically, SHISAL1, SLC43A3, NBAT1, GeneMANIA, identifying oncogenes, such as SLC43A3,
PDZK1IP1, ACKR3, KCNN3, ATOH8, IGFBP7, GPR35, ACKR3, KCNN3, LEMD1, GPR35, WNT7A, F2RL3, and
WNT7A, and F2RL3 were predicted to harbor one or ANO5, along with tumor suppressors, such as NBAT1,
two FXR1 binding sites (Table 2). These predictions were PDZK1IP1, NECAB2, ATOH8, and IGFBP7, that are
supported by existing crosslinking immunoprecipitation potentially co-expressed with FXR1 (Figure 6). This
sequencing (CLIP-seq) data, which independently complex network involves multiple interaction types,
validated the presence of FXR1 binding regions within the including co-expression and genetic interactions (Table 3).
CLIP-seq peaks on these mRNAs, further substantiating Functional enrichment analysis indicated that these
the accuracy of the predictions. In contrast, no FXR1 co-expressed genes are primarily associated with mRNA
binding sites were identified on the mRNAs of NECAB2, splicing, cellular stress response, physiological function,
LEMD1, and ANO5, suggesting that these particular and tumorigenesis. The results suggest that FXR1 may
transcripts may not be direct targets of FXR1 under the regulate RNA stability and translation, potentially
conditions tested (Table 2). The absence of binding sites on enhancing cancer progression by stabilizing mRNAs
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 7 doi: 10.36922/gpd.5068