Page 23 - GPD-4-2
P. 23
Gene & Protein in Disease lncRNAs dysregulation in diabetes and its complications
A
B
C
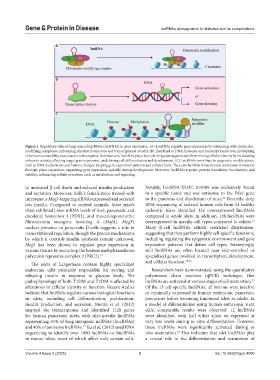
Figure 1. Regulatory roles of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in gene expression. (A) LncRNAs regulate gene expression by interacting with chromatin-
modifying complexes, influencing chromatin structure and transcriptional activity. (B) They bind to DNA, histones, and transcription factors, modulating
chromatin accessibility to activate or silence genes. As enhancers, lncRNAs play a key role in regulating genes and determining cellular identity by modulating
enhancer activity, affecting target gene expression, and driving cell differentiation and development. (C) LncRNAs contribute to epigenetic modifications,
such as DNA methylation and histone changes, shaping gene expression patterns and cellular traits. They also facilitate biomolecular condensate formation
through phase separation, organizing gene expression spatially during development. Moreover, lncRNAs regulate protein translation, localization, and
stability, influencing cellular processes, such as metabolism and signaling.
to increased β-cell death and reduced insulin production Notably, lincRNA-XLOC 019089 was exclusively found
and secretion. Moreover, Balb/c female mice treated with in a specific tissue and was antisense to the Pdx1 gene
intravenous Meg3-targeting siRNAs expressed and secreted in the pancreas and duodenum of mice. Recently, deep
16
less insulin. Compared to control animals, these mice’s RNA sequencing of isolated human cells from 11 healthy
islets exhibited lower mRNA levels of Ins2, pancreatic and cadaveric islets identified 132 overexpressed lincRNAs
duodenal homeobox 1 (PDX1), and musculoaponeurotic compared to whole islets. In addition, 148 lncRNAs were
17
fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog A (MafA). Meg3’s overexpressed in specific cell types compared to others.
nuclear presence in pancreatic β-cells suggests a role in Many β-cell lncRNAs exhibit restricted distribution,
transcriptional regulation, though the precise mechanisms suggesting that they perform highly cell-specific functions,
by which it controls insulin synthesis remain unknown. including regulating the epigenetic environment and gene
Meg3 has been shown to regulate gene expression in expression patterns that define cell types. Interestingly,
various tissues by recruiting the histone methyltransferase islet lncRNAs are often located near islet-enriched or
polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2). 14 specialized genes involved in transcription, development,
The islets of Langerhans contain highly specialized and cellular function. 15,16
endocrine cells primarily responsible for storing and Researchers have demonstrated, using the quantitative
releasing insulin in response to glucose levels. The polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) technique, that
pathophysiology of both T1DM and T2DM is affected by lncRNAs are activated at various stages of cell maturation.
15
alterations in cellular identity or function. Recent studies Of the 13 cell-specific lncRNAs, all but one were inactive
indicate that lncRNAs regulate various biological functions or minimally expressed in human embryonic pancreatic
in islets, including cell differentiation, proliferation, precursors before becoming functional islets in adults. In
insulin production, and secretion. Morán et al. (2012) a model of differentiation using human embryonic stem
mapped the transcriptome and identified 1128 genes cells, comparable results were observed: 12 lncRNAs
for human pancreatic islets, with islet-specific lncRNAs were identified, with half either silent or expressed at
representing 55% of long intergenic ncRNAs (lincRNAs) very low levels during in vitro differentiation. However,
15
and 40% of antisense lncRNAs. Ku et al. (2012) used RNA these lncRNAs were significantly activated during in
sequencing to identify over 1000 lncRNAs or lincRNAs vivo maturation. This indicates that islet lncRNAs play
18
in mouse islets, most of which affect only certain cells. a crucial role in the differentiation and maturation of
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 3 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4000