Page 25 - GPD-4-2
P. 25
Gene & Protein in Disease lncRNAs dysregulation in diabetes and its complications
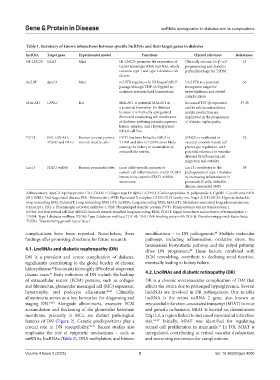
Table 1. Summary of known interactions between specific lncRNAs and their target genes in diabetes
lncRNA Target gene Experimental model Functions Clinical relevance References
HI-LNC25 GLIS3 Mice HI-LNC25 promotes the expression of Clinically relevant for β-cell 15
GLIS3 messenger RNA (mRNA), which programming and diabetes
contains type 1 and type 2 diabetes risk pathophysiology for T2DM
factors.
lncLST ApoC2 Mice ncLSTR regulates the FXR/apoC2/PLP LncLSTR is a potential 36
passage through TDP-43/Cyp8b1 to therapeutic target for
maintain systemic lipid homeostasis. hyperlipidemia and related
complications
MALAT1 CPNL1 Rat MALAT1 is potential MALAT1 is Increased TGF-β expression 37,38
a potential biomarker for diabetes and its role in extracellular
because it is markedly upregulated matrix production are
fibers and conducting cell membranes implicated in the progression
of diabetes-suffering patients, aqueous of diabetic nephropathy
humor samples, and a hyperglycemic
RF/6A cell line.
PVT1 FN1, COL4A1, Human coronary artery PVT1 has been linked to ESRD in SENCR is implicated in 32
TGFB1 and PAI‑1 smooth muscle cells T1DM and also in T2DM, most likely vascular smooth muscle cell
causing the kidney to accumulate an phenotype regulation, with
extracellular matrix. potential relevance to vascular
diseases by influencing cell
migration and stability
Lnc13 STAT1 mRNA Human pancreatic islets In an allele-specific manner, to Lnc13 contributes to the 39
sustain-cell inflammation, Lnc13-PCBP2 pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes
interactivity controls STAT1 mRNA by increasing inflammation in
secureness. pancreatic β-cells, linked to
disease-associated SNPs
Abbreviations: ApoC2: Apolipoprotein C2; COL4A1: Collagen type IV alpha 1; CPNL1: Carboxypeptidase N, polypeptide 1; Cyp8b1: Cytochrome P450
8B1; ESRD: End-stage renal disease; FN1: Fibronectin 1; FXR: Farnesoid X receptor; GLIS3: GLIS family zinc finger 3; HI-LNC25: Hypoxia-inducible
long noncoding RNA 25;lncLST: Long noncoding RNA LST; lncRNA: Long noncoding RNA; MALAT1: Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma
transcript 1; PAI-1: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; PLP: Phospholipid transfer protein; PVT1: Plasmacytoma variant translocation 1;
RF/6A: Rat fetal retinal cell line; SENCR: Smooth muscle-enriched long noncoding RNA; STAT1: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1;
T1DM: Type 1 diabetes mellitus; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; TDP-43: TAR DNA-binding protein 43; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor beta;
TGFB1: Transforming growth factor beta 1.
complications have been reported. Nonetheless, these modifications – in DN pathogenesis. Multiple molecular
48
findings offer promising directions for future research. pathways, including inflammation, oxidative stress, the
hexosamine biosynthetic pathway, and the polyol pathway,
4.1. LncRNAs and diabetic nephropathy (DN) drive DN progression. These factors, combined with
49
DN is a prevalent and severe complication of diabetes, ECM remodeling, contribute to declining renal function,
significantly contributing to the global burden of chronic eventually leading to kidney failure.
kidney disease. It accounts for roughly 40% of end-stage renal
40
disease cases. Early indicators of DN include the buildup 4.2. LncRNAs and diabetic retinopathy (DR)
41
of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, such as collagen DR is a chronic microvascular complication of DM that
and fibronectin, glomerular mesangial cell (MC) expansion, affects the retina due to prolonged hyperglycemia. Several
hypertrophy, and podocyte effacement. 42,43 Clinically, lncRNAs are involved in DR pathogenesis. One notable
albuminuria serves as a key biomarker for diagnosing and lncRNA is the retina ncRNA 2 gene, also known as
staging DN. 44,45 Alongside albuminuria, excessive ECM myocardial infarction-associated transcript (MIAT) in mice
accumulation and thickening of the glomerular basement and gomafu in humans. MIAT is located on chromosome
membrane, primarily in MCs, are distinct pathological 22q12.1, a region linked to increased myocardial infarction
features of DN (Figure 2). Genetic predispositions play a risk. 56,57 Initially, MIAT was identified for regulating
crucial role in DN susceptibility. 46,47 Recent studies also retinal cell proliferation in mammals. In DR, MIAT is
58
emphasize the role of epigenetic mechanisms – such as upregulated, contributing to retinal vascular dysfunction
miRNAs, lncRNAs (Table 2), DNA methylation, and histone and worsening microvascular complications.
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4000