Page 27 - GPD-4-2
P. 27
Gene & Protein in Disease lncRNAs dysregulation in diabetes and its complications
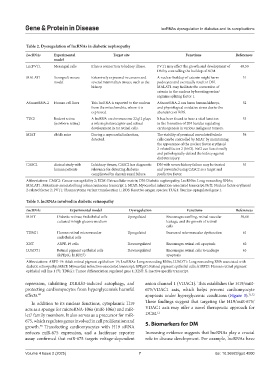
Table 2. Dysregulation of lncRNAs in diabetic nephropathy
LncRNAs Experimental Target site Functions References
model
LncPVT1 Mesangial cells It has a connection to kidney illness. PVT1 may affect the growth and development of 40,50
DN by controlling the buildup of ECM.
MALAT1 Xenograft mouse Extensively expressed in cancers and A nuclear buildup of catenin might harm 51
model several mammalian tissues, such as the podocytes and eventually result in DN.
kidney. MALAT1 may facilitate the conversion of
catenin in the nucleus by boosting serine/
arginine splicing factor 1.
ASncmtRNA-2 Human cell lines This lncRNA is exported to the nucleus ASncmtRNA-2 can harm human kidneys, 52
from the mitochondria, where it is and physiological oxidative stress due to the
expressed. abundance of ROS.
TUG1 Rodent retina A lncRNA on chromosome 22q12 plays It has been found to have a vital function 53
(newborn retina) a role in photoreceptor and retinal in the formation of DN besides regulating
development in rat retinal cells. carcinogenesis in various malignant tumors.
MIAT db/db mice During a myocardial infarction, The viability of proximal convoluted tubule 54
detected. cells can be controlled by MIAT by maintaining
the appearance of the nuclear factor erythroid
2-related factor 2 (Nrf2). Nrf2 can functionally
and pathologically defend the kidney against
diabetes injury.
CASC2 clinical study with In kidney tissues, CASC2 has diagnostic DN with severe kidney failure may be treated 55
human patients relevance for detecting diabetes and prevented using CASC2 as a target and
complicated by chronic renal failure. predictive factor.
Abbreviations: CASC2: Cancer susceptibility 2; ECM: Extracellular matrix; DN: Diabetic nephropathy; LncRNAs: Long noncoding RNAs;
MALAT1: Metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1; MIAT: Myocardial infarction-associated transcript; Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid
2-related factor 2; PVT1: Plasmacytoma variant translocation 1; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TUG1: Taurine-upregulated gene 1.
Table 3. lncRNAs involved in diabetic retinopathy
LncRNAs Experimental model Dysregulation Functions References
MIAT Diabetic retinas; Endothelial cells Upregulated Encourages swelling, retinal vascular 59,60
cultured in high glucose medium leakage, and the growth of retinal
cells
TDRG1 Human retinal microvascular Upregulated Increased microvascular dysfunction 61
endothelial cells
XIST ARPE-19 cells Downregulated Encourages retinal cell apoptosis 62
LUADT1 Retinal pigment epithelial cells Downregulated Encourages retinal cells to undergo 63
(RPEpiC, h1RPE7) apoptosis
Abbreviations: ARPE-19: Adult retinal pigment epithelium 19; LncRNAs: Long noncoding RNAs; LUADT1: Long noncoding RNA associated with
diabetic retinopathy; MIAT: Myocardial infarction-associated transcript; RPEpiC: Retinal pigment epithelial cells; h1RPE7: Human retinal pigment
epithelial cell line 1 (7); TDRG1: Tumor differentiation regulated gene 1; XIST: X-inactive specific transcript.
repression, inhibiting DIRAS3-induced autophagy, and anion channel 1 (VDAC1). This establishes the H19/miR-
protecting cardiomyocytes from hyperglycemia’s harmful 675/VDAC1 axis, which helps prevent cardiomyocyte
effects. 69 apoptosis under hyperglycemic conditions (Figure 3). 71,72
In addition to its nuclear functions, cytoplasmic H19 These findings suggest that targeting the H19/miR-675/
acts as a sponge for microRNA-106a (miR-106a) and miR- VDAC1 axis may offer a novel therapeutic approach for
let7 family members. It also serves as a precursor for miR- DCM. 12
675, which regulates genes involved in cell proliferation and 5. Biomarkers for DM
growth. Transfecting cardiomyocytes with H19 siRNA
70
reduces miR-675 expression, and a luciferase reporter Increasing evidence suggests that lncRNAs play a crucial
assay confirmed that miR-675 targets voltage-dependent role in disease development. For example, lncRNAs have
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 7 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4000