Page 28 - GPD-4-2
P. 28
Gene & Protein in Disease lncRNAs dysregulation in diabetes and its complications
aberrant expression in various T2DM-related conditions.
The human HOTAIR, a 2364-bp lncRNA derived from
a 6449-bp gene on chromosome 12q13.13, contains six
exons. Its half-life is cell-specific, with about 4 hours in
81
HeLa cells. 82,83 Elevated HOTAIR expression in individuals
with DR may serve as a marker to distinguish DR from
non-DR.
Moreover, hyperglycemia upregulates HOTAIR
expression in human retinal endothelial cells, suggesting
84
its role in DR progression. In DCM, HOTAIR promotes
Akt phosphorylation, aiding cardiomyocyte survival.
85
A study in mice on a high-fat diet (HFD) also reported
increased HOTAIR expression, reinforcing its strong link
to T2DM. 86
LncRNAs significantly regulate cellular responses and
diseases. Growing evidence supports their potential as
biomarkers for diagnosing and predicting cancer, viral
infections, and autoimmune disorders. 87,89 They are also
linked to diabetes, with research highlighting their distinct
expression patterns. Wang et al. (2013) used qRT-PCR
on serum from 96 T2DM patients, finding elevated HOX
antisense intergenic RNA as a distinguishing feature and
potential noninvasive diagnostic marker and independent
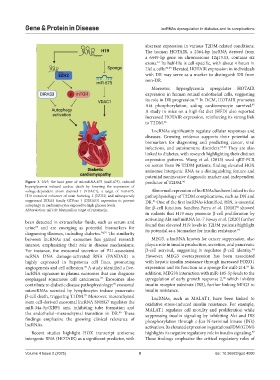
Figure 3. H19, the host gene of microRNA-675 (miR-675), reduced predictor of T2DM. 90
hyperglycemia-induced cardiac death by lowering the expression of
voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC1), a target of miR-675. Abnormal expression of lncRNAs has been linked to the
H19 recruited enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) and subsequently pathophysiology of T2DM complications, such as DN and
suppressed DIRAS family GTPase 3 (DIRAS3) expression to prevent DR. One of the first lncRNAs identified, H19, is essential
91
autophagy in cardiomyocytes exposed to high glucose levels. for β-cell function. Sanchez-Parra et al. (2018) showed
92
Abbreviation: mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin.
in rodents that H19 may promote β-cell proliferation by
activating Akt and miRNA let-7 Fawzy et al. (2020) further
been detected in extracellular fluids, such as serum and found that elevated H19 levels in T2DM patients highlight
urine and are emerging as potential biomarkers for its potential as a biomarker for insulin resistance. 93
73
diagnosing illnesses, including diabetes. 74,75 The similarity
between lncRNAs and exosomes has gained research MEG3, a lncRNA known for cancer suppression, also
interest, emphasizing their role in disease mechanisms. plays a role in insulin production, secretion, and pancreatic
For instance, the exosomal secretion of P21-associated β-cell survival, suggesting it regulates β-cell identity.
94
ncRNA DNA damage-activated RNA (PANDAR) is However, MEG3 overexpression has been associated
highly expressed in hepatoma cell lines, promoting with hepatic insulin resistance through increased FOXO1
angiogenesis and cell adhesion. A study identified a five- expression and its function as a sponge for miR-214. In
95
76
lncRNA signature in plasma exosomes that can diagnose addition, MEG3’s interaction with miR-185-5p leads to the
96
77
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Exosomes also upregulation of early growth response 2, which inhibits
contribute to diabetic disease pathophysiology; exosomal insulin receptor substrate (IRS), further linking MEG3 to
78
microRNAs secreted by lymphocytes induce pancreatic insulin resistance.
β-cell death, triggering T1DM. Moreover, mesenchymal LncRNAs, such as MALAT1, have been linked to
79
stem cell-derived exosomal lncRNA SNHG7 regulates the oxidative stress-induced insulin resistance. For example,
miR-34a-5p/XBP1 axis, inhibiting tube formation and MALAT1 regulates cell motility and proliferation while
the endothelial–mesenchymal transition in DR. These suppressing insulin signaling by inhibiting Akt and IRS
80
findings emphasize the growing clinical relevance of phosphorylation through c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNk)
lncRNAs. activation. Its elevated expression in gestational DM (GDM)
Recent studies highlight HOX transcript antisense highlights its negative regulatory role in insulin signaling.
97
intergenic RNA (HOTAIR) as a significant predictor, with These findings emphasize the critical regulatory roles of
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 8 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4000