Page 26 - GPD-4-2
P. 26
Gene & Protein in Disease lncRNAs dysregulation in diabetes and its complications
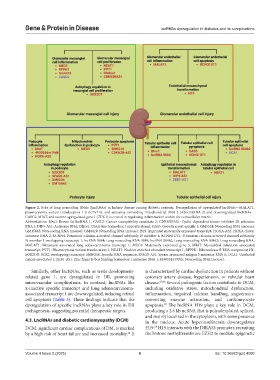
Figure 2. Role of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in kidney disease among diabetic patients. Dysregulation of upregulated lncRNAs—MALAT1,
plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 (LncPVT1), and antisense noncoding mitochondrial RNA-2 (ASncmtRNA-2) and downregulated lncRNAs—
CASC2, MIAT, and taurine-upregulated gene 1 (TUG1) is crucial in regulating inflammation within the extracellular matrix.
Abbreviations: Blnc1: Brown fat lncRNA 1; CASC2: Cancer susceptibility candidate 2; CDKN2BAS1: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2B antisense
RNA 1; DIP5-AS1: Antisense RNA; Dlxos1: Distal-less homeobox 1 opposite strand; GAS5: Growth arrest-specific 5; GM5524: Noncoding RNA (mouse);
GM15645: Non-coding RNA (mouse); GM4419: Noncoding RNA (mouse); H19: Imprinted maternally expressed transcript; HOXA-AS2: HOXA cluster
antisense RNA 2; KCNN4: Potassium calcium-activated channel subfamily N member 4; KCNN1OT1: Potassium calcium-activated channel subfamily
N member 1 overlapping transcript 1; lncRNA 9884: Long noncoding RNA 9884; lncRNA 00462: Long noncoding RNA 00462; Long noncoding RNA;
MALAT1: Metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1; MEG3: Maternally expressed gene 3; MIAT: Myocardial infarction associated
transcript; PVT1: Plasmacytoma variant translocation 1; NEAT1: Nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1; RPPH1: Ribonuclease P RNA component H1;
SOX2OT: SOX2 overlapping transcript; SHNG16: Specific RNA sequence; SPAG5-AS1: Sperm associated antigen 5 antisense RNA 1; UCA1: Urothelial
cancer-associated 1; ZEB1-AS1: Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1 antisense RNA 1; 4930551F19Rik: Noncoding RNA (mouse).
Similarly, other lncRNAs, such as testis development- is characterized by cardiac dysfunction in patients without
related gene 1, are dysregulated in DR, promoting coronary artery disease, hypertension, or valvular heart
microvascular complications. In contrast, lncRNAs like disease. 65,66 Several pathogenic factors contribute to DCM,
x-inactive specific transcript and lung adenocarcinoma- including oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction,
associated transcript 1 are downregulated, inducing retinal inflammation, impaired calcium handling, angiotensin-
cell apoptosis (Table 3). These findings indicate that the converting enzyme activation, and cardiomyocyte
dysregulation of specific lncRNAs plays a key role in DR apoptosis. The lncRNA H19 plays a key role in DCM,
67
pathogenesis, suggesting potential therapeutic targets. producing a 2.6 kb ncRNA that is polyadenylated, spliced,
and mainly localized in the cytoplasm, with some presence
4.3. LncRNAs and diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) in the nucleus. Acute hyperinsulinemia downregulates
68
DCM, significant cardiac complications of DM, is marked H19. H19 interacts with the DIRAS3 promoter, recruiting
by a high risk of heart failure and increased mortality. It the histone methyltransferase EZH2 to mediate epigenetic
64
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/gpd.4000