Page 34 - GPD-4-3
P. 34
Gene & Protein in Disease TNFA polymorphism and risk of endometriosis
A
B
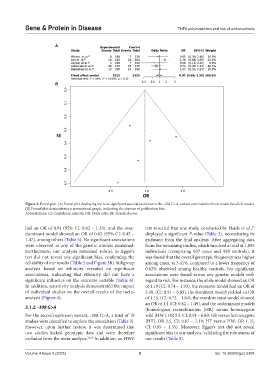
Figure 3. Forest plot. (A) Forest plot displaying the non-significant association between the -238 G>A variant and endometriosis under the allele model.
(B) Funnel plot demonstrates a symmetrical graph, indicating the absence of publication bias.
Abbreviations: CI: Confidence interval; OR: Odds ratio; SE: Standard error.
had an OR of 0.91 (95% CI: 0.62 – 1.33), and the over- test revealed that one study, conducted by Hsieh et al.,
13
dominant model showed an OR of 0.82 (95% CI: 0.45 – displayed a significant P-value (Table 3), necessitating its
1.47), among others (Table 5). No significant associations exclusion from the final analysis. After aggregating data
were observed in any of the genetic models examined. from the remaining studies, which involved a total of 1,895
Furthermore, our analysis remained robust, as Egger’s individuals (comprising 937 cases and 958 controls), it
test did not reveal any significant bias, confirming the was found that the overall genotypic frequency was higher
reliability of our results (Table 5 and Figure 3B). Subgroup among cases, at 3.41%, compared to a lower frequency of
analysis based on ethnicity revealed no significant 0.62% observed among healthy controls. No significant
associations, indicating that ethnicity did not have a associations were found across any genetic models with
significant influence on the outcome variable (Table 6). regard to risk. For instance, the allele model showed an OR
In addition, sensitivity analysis demonstrated the impact of 1.19 (CI: 0.74 – 1.93), the recessive model had an OR of
of individual studies on the overall results of the meta- 2.48, (CI: 0.91 – 6.83), the dominant model yielded an OR
analysis (Figure 4). of 1.15, (CI: 0.72 – 1.84), the overdominant model showed
an OR of 1.1 (CI: 0.82 – 1.49), and the codominant models
3.1.2. -308 G>A (homologous recombination [HR] versus homozygous
For the second upstream variant, -308 G>A, a total of 10 wild [HW]: OR 2.5, CI: 0.91 – 6.89; HR versus heterozygote
studies were identified to explore the association (Table 3). [HT]: OR 2.5, CI: 0.87 – 7.19; HT versus HW: OR 1.15,
However, upon further review, it was determined that CI: 0.85 – 1.55). Moreover, Egger’s test did not reveal
two studies lacked genotypic data and were therefore significant bias in our analysis, validating the robustness of
excluded from the meta-analysis. 12,14 In addition, an HWE our results (Table 5).
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 8 doi: 10.36922/gpd.5204