Page 35 - GPD-4-3
P. 35
Gene & Protein in Disease TNFA polymorphism and risk of endometriosis
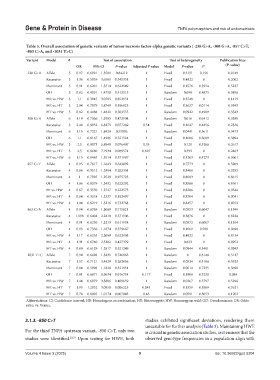
Table 5. Overall association of genetic variants of tumor necrosis factor‑alpha genetic variants (‑238 G>A, ‑308 G>A, ‑857 C>T,
‑863 C>A, and ‑1031 T>C)
Variant Model # Test of association Test of heterogeneity Publication bias
OR 95% CI P‑value Adjusted P value Model P‑value I 2 (P‑value)
-238 G>A Allele 5 0.97 0.6921 – 1.3501 0.84212 1 Fixed 0.3151 0.156 0.9149
Recessive 3 1.36 0.5039 – 3.6581 0.545358 1 Fixed 0.4822 0 0.2062
Dominant 5 0.91 0.6201 – 1.3314 0.622949 1 Fixed 0.1576 0.3954 0.5227
OD 5 0.82 0.4591 – 1.4758 0.513515 1 Random 0.099 0.4875 0.3856
HR vs. HW 3 1.1 0.3945 – 3.0785 0.852951 1 Fixed 0.3748 0 0.1419
HR vs. HT 3 2.04 0.7079 – 5.8749 0.186825 1 Fixed 0.3637 0.0114 0.3543
HT vs. HW 5 0.82 0.4488 – 1.4821 0.503555 1 Random 0.0922 0.4989 0.3543
-308 G>A Allele 6 1.19 0.7366 – 1.9305 0.473908 1 Random 0.016 0.6412 0.3388
Recessive 3 2.48 0.9052 – 6.8275 0.077269 0.54 Fixed 0.1647 0.4456 0.2336
Dominant 6 1.15 0.7221 – 1.8429 0.55006 1 Random 0.0441 0.5611 0.3473
OD 6 1.1 0.8167 – 1.4906 0.521524 1 Fixed 0.1606 0.3689 0.3894
HR vs. HW 3 2.5 0.9073 – 6.8940 0.076407 0.53 Fixed 0.121 0.5266 0.2617
HR vs. HT 3 2.5 0.8680 – 7.1934 0.089574 0.627 Fixed 0.393 0 0.2463
HT vs. HW 6 1.15 0.8485 – 1.5514 0.371987 1 Fixed 0.1203 0.4273 0.3601
-857 C>T Allele 4 0.95 0.7817 – 1.1643 0.643092 1 Fixed 0.7773 0 0.5969
Recessive 4 0.66 0.3512 – 1.2494 0.203301 1 Fixed 0.8408 0 0.0295
Dominant 4 1 0.7925 – 1.2529 0.975723 1 Fixed 0.8083 0 0.8615
OD 4 1.06 0.8379 – 1.3432 0.623292 1 Fixed 0.8588 0 0.8101
Hr vs. HW 4 0.67 0.3550 – 1.2727 0.222573 1 Fixed 0.8286 0 0.0544
HR vs. HT 4 0.64 0.3318 – 1.2337 0.182497 1 Fixed 0.8704 0 0.0041
HT vs. HW 4 1.04 0.8219 – 1.3216 0.732768 1 Fixed 0.8457 0 0.9072
-863 C>A Allele 4 0.94 0.6769 – 1.3069 0.715021 1 Random 0.0553 0.6047 0.1949
Recessive 4 1.198 0.6404 – 2.2410 0.571906 1 Fixed 0.5876 0 0.8224
Dominant 4 0.91 0.6230 – 1.3213 0.611938 1 Random 0.0572 0.6007 0.1354
OD 4 0.93 0.7356 – 1.1874 0.579667 1 Fixed 0.1069 0.508 0.0698
HR vs. HW 4 1.17 0.6235 – 2.2009 0.622903 1 Fixed 0.4822 0 0.8134
HR vs. HT 4 1.31 0.6760 – 2.5202 0.427379 1 Fixed 0.823 0 0.9952
HT vs. HW 4 0.89 0.6129 – 1.2817 0.521249 1 Random 0.0844 0.5481 0.0943
-1031 T>C Allele 7 0.94 0.6628 – 1.3431 0.746865 1 Random 0 0.8146 0.5127
Recessive 7 1.57 0.7121 – 3.4829 0.262056 1 Random 0.0524 0.5186 0.5923
Dominant 7 0.84 0.5998 – 1.1828 0.321831 1 Random 0.0014 0.7235 0.3698
OD 7 0.81 0.6871 – 0.9634 0.016734 0.117 Fixed 0.1808 0.3238 0.084
HR vs. HW 7 1.44 0.6079 – 3.3886 0.409659 1 Random 0.0267 0.5797 0.5296
HR vs. HT 7 1.93 1.2052 – 3.0958 0.006225 0.043 Fixed 0.1559 0.3569 0.7621
HT vs. HW 7 0.78 0.6005 – 1.0174 0.067043 0.46 Random 0.0591 0.5053 0.1702
Abbreviations: CI: Confidence interval; HR: Homologous recombination; HT: Heterozygote; HW: Homozygous wild; OD: Overdominant; OR: Odds
ratio; vs: Versus.
3.1.3. -850 C>T studies exhibited significant deviations, rendering them
unsuitable for further analysis (Table 3). Maintaining HWE
For the third TNFA upstream variant, -850 C>T, only two is crucial in genetic association studies, as it ensures that the
studies were identified. 29,31 Upon testing for HWE, both observed genotype frequencies in a population align with
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 9 doi: 10.36922/gpd.5204