Page 23 - GTM-1-1
P. 23
Global Translational Medicine Anticancer effect of S. xanthocarpum on KB cell line
A
B
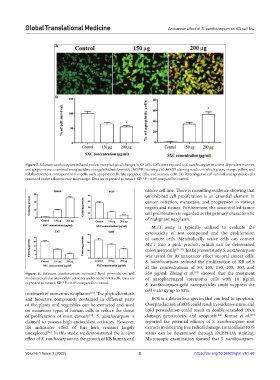
Figure 5. Solanum xanthocarpum induced nuclear morphological changes in KB cells. Cells were exposed to S. xanthocarpum in a time‐dependent manner,
and apoptosis was examined using acridine orange/ethidium bromide (AO/EB) staining. (A) AO/EB staining results, in which green, orange, yellow, and
red fluorescences correspond to live cells, early apoptotic cells, late apoptotic cells, and necrotic cells. (B) Percentages of cell survival and apoptotic cells
examined under a fluorescence microscope. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 compared to control.
cancer cell line. There is mounting evidence showing that
uninhibited cell proliferation is an essential element in
cancer initiation, metastasis, and progression in various
organs and tissues. Furthermore, the uncontrolled tumor
cell proliferation is regarded as the primary characteristic
of malignant neoplasm.
MTT assay is typically utilized to evaluate the
cytotoxicity of test compound and the proliferation
of cancer cells. Metabolically active cells can convert
MTT into a pink product, which can be determined
colorimetrically [21,22] . In the present study, S. xanthocarpum
was tested for its anticancer effect on oral cancer cells.
S. xanthocarpum reduced the proliferation of KB cells
at the concentrations of 50, 100, 150, 200, 300, and
[23]
Figure 6. Solanum xanthocarpum activated lipid peroxidation and 350 µg/ml. Zhang et al. showed that the treatment
modulated cellular antioxidant activities and content in KB cells. Data are of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells with 10 µg/ml
expressed as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 compared to control. S. xanthocarpum-gold nanoparticles could suppress the
cell viability up to 53%.
treatment of numerous neoplasms . The phytochemicals
[18]
and bioactive compounds contained in different parts ROS is a deleterious species that can lead to apoptosis.
of the plants and vegetables can be extracted and used Overproduction of ROS could result in oxidative stress, and
on numerous types of human cells to reduce the threat lipid peroxidation could resuls in double-stranded DNA
[24]
[25]
of proliferation of most cancers . S. xanthocarpum is damage, genotoxicity, and apoptosis. Kumar et al.
[19]
claimed to possess high antioxidant activities. However, reported the potential efficacy of S. xanthocarpum root
the anticancer effect of this herb remains largely extracts in deterring free radical damage. Intracellular ROS
unexplored . In this study, we demonstrated the in vitro status can be determined through DCFH-DA staining.
[20]
effect of S. xanthocarpum on the growth of KB human oral Microscopic examination showed that S. xanthocarpum-
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2022) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v1i1.68